Note: สำหรับ Blog นี้ ผมย้ายมาจาก Notion ที่เขียนไว้ตอนเดือน 9-10 ปีที่แล้วนะครับ บาง Service อย่าง Azure AD มีเปลี่ยนชื่อเป็น Microsoft Entra ID เป็นต้นครับ
Configure Azure Active Directory
- Azure AD feature:
- Single sign-on (SSO) access
- Ubiquitous device support: ใช้ได้กับหลากหลาย iOS, Android, Windows
- Secure remote access: MFA / Conditional Access / RBAC
- Cloud extensibility: consistent set of users, groups, passwords, and devices across environments
- Sensitive data protection: ไปหาเพิ่ม
- Self-service support: self-service app access / password reset
- Azure Active Directory (product that provides the identity service) key components
- Identity is an object that can be authenticated user/ app นับด้วยนะ
- Account an identity that has data associated
- Azure AD account Account ที่สร้างจาก Azure AD หรือ 365
- Azure tenant (directory) single dedicated and trusted instance of Azure AD ปกติ 1 องค์กร จัดเป็น 1 tenant อยู่
- Azure subscription
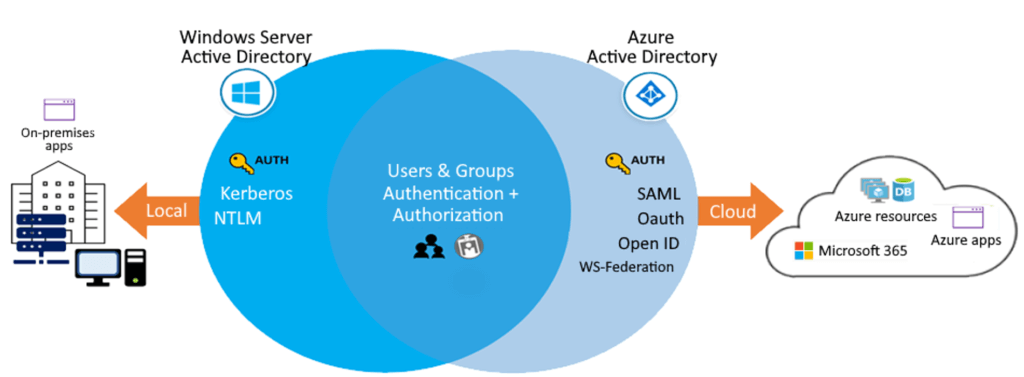
- Compare Active Directory Domain Services (Windows Server) to Azure Active Directory หลักๆตามรูปข้างบน
- Azure AD - Federation services (คล้ายๆ FB Sign ins) / Managed service
- Azure AD
- full identity solution HTTP and HTTPS พวก Web OpenID SAML OAuth
- AD DS ได้แต่แบบ kerberos / NTLM
- Flat structure: Azure AD users and groups are created in a flat structure. There are no organizational units (OUs) or group policy objects (GPOs). อันนั้น AD DS

- Azure AD Join vs Registration
- Azure AD Join - Win10 + Join Device + Login Azure AD และมีอื่นๆ
- SSO
- Enterprise state roaming //Sync User Setting
- Access to Microsoft Store for Business
- Windows Hello
- Restriction of access ตาม compliance policies.
- Seamless access to on-premises resources
- Azure AD Registration - BYOD + Personal Account กับ Azure ADล
- Azure AD Join - Win10 + Join Device + Login Azure AD และมีอื่นๆ
- การจัดการ mobile device management (MDM) เช่น Microsoft Intune เพิ่ม conditional access rules
- Implement Azure Active Directory self-service password reset
- SSPR feature
- Global Administrator privileges to manage SSPR options
- SSPR uses a security group to limit the users
- All user accounts in your organization must have a valid license to use SSPR
- Consider
- who can reset their passwords - มี 3 แบบ None, Selected (อาจจะเอามาลอง หรือ กำหนด Groupที่ใช้), All.
- authentication methods เช่น Email / Security Code / Security Question
- combining methods for stronger security
- Configure Azure Active Directory: Knowledge Check
Azure AD: Configure user and group accounts
- Create user accounts
- มี 3 แบบ Cloud
- identity (Azure AD)
- Directory-synchronized identity (เอามาจาก On Premise AD)
- Guest user (External User ที่ต้องการมาใช้ Resource เรา เช้น Outsource Dev)
- Note: 1 Organization อาจจะมี user accounts วางแผน และ combination ให้เหมาะสม
- Create User (cloud identity accounts_
- administrator Create / Invite แต่มีสิ่งที่ต้องสนใจ ดังนี้
- user profile data อะไรที่ใช้ หรือไม่ใช้บ้าง อาจจะติดให้เรียบร้อย เพราะ บาง Feature อาจจะต้องการใช้ เช่น Conditional Access ต้องการ Location จะได้ไม่เสียเวลามาตามแก้
- restore options for deleted accounts - 30 วัน
- gathered account data. Collect sign-in/ audit log เอามา Monitor +วิเคราะห์ในอนาคตได้
- Create bulk user accounts : administrator เตรียม csv เอาไว้ หรือ download template จาก azure แต่มีสิ่งที่ต้องสนใจ
- naming conventions ทำให้ unique จะได้ลด Effort Error
- initial passwords + force เปลี่ยน
- strategies for minimizing errors อาจจะแบ่งทำ และดูผลจาก Bulk operation results
- Create group accounts
- 2 Group Type
- Security groups จัดการ user+device + set permissions สะดวก
- Microsoft 365 groups - เพิ่ม shared mailbox, calendar, files, SharePoint site + group access for guest users
- Group Access rights
- Assigned (กำหนดรายคน / group แยกสิทธิได้)
- Dynamic user ดูตาม Profile (attributes) ถ้าเรากำหนดตรงตามเงื่อนไข จะได้สิทธินั้นไป ถ้าไม่ตรงเอาออกให้ด้วย Auto
- Dynamic device เหมือน Dynamic user ดู device แทน user
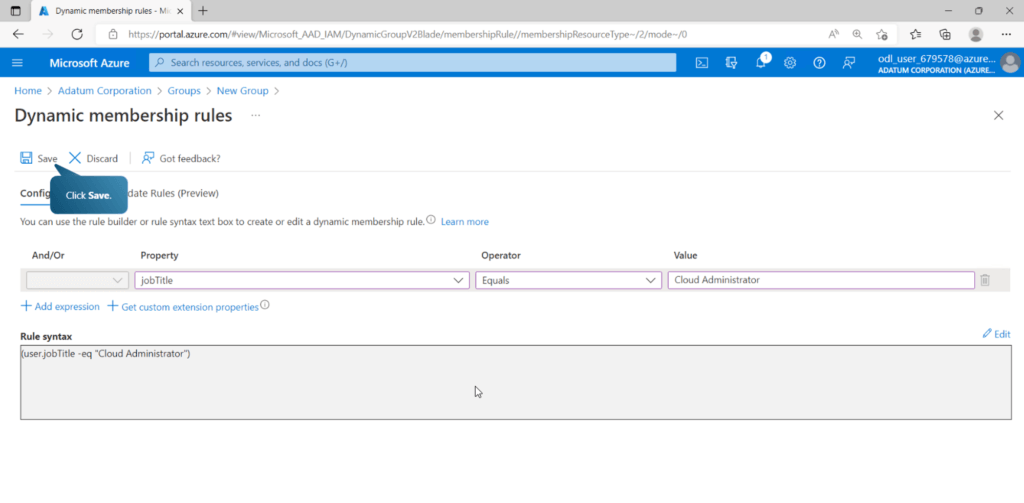
- Create administrative units (Admin หน่วยงานย่อยสิทธิจะน้อยกว่า Global Admin / Privileged Role Administrator) อะไรที่ควรดูบ้าง ****management tools / role requirements / Scope of administrative units
- Lab: Configure user and group accounts Interactive lab simulation
- Configure user and group accounts: Knowledge Check
Configure subscriptions
- Identify Azure regions
- ใช้กับ Service อื่นๆนะ เพราะ Azure AD, Azure Traffic Manager, Azure DNS ไม่สนใจ regions ล่มหมดโลก ถ้าพัง
- ส่วน Service อื่นๆ พิจารณาจาก Region Pair ให้ดูจาก Physical isolation (ห่าง 300 miles) / Platform-provided replication (Geo-Redundant Storage) / Region recovery order (นึกถึงเคสที่ SEA Down ปล SEA ไม่มี region pair ) / Sequential updates / Data residency / Service ที่ให้บริการดูบางทีมี VM Size นี้ แต้่บางทีไม่มี
- Subscription ส่วนนึงเอามาแยก Cost ให้ชัดเจนของแต่ละแผนก หรือ Enviroment รูปแบบการจ่ายเงินด้วย Dev Pay As You Go แต่ Prod ทำสัญญายาว
- 1 Azure account มีได้ n subscription / n Azure account จะใช้ 1 subscription
- Azure subscription มี 4 แบบ Enterprise agreement / Microsoft reseller / Microsoft partner (Consult Technical ได้) / Personal free account (Pay As you Go)
- ถ้าทดสอบเริ่มจาก Trial Free 200 usd > Student 12 เดือน Limit 50 usd มั้ง > Pay-As-You-Go > Enterprise Agreement (สัญญายาว)
- Cost Management เอาไว้ดูยอดที่ใช้งานจริงๆ มีส่วนที่สนใจ cost analysis ดูว่าใช้อะไรไปบ้าง / budget options เช่่น บอกว่าเกินไปแค่ไหน / recommendations จากพฤติกรรมการใช้งาน
- resource tagging ทำ metadata ของ resource เอาไว้ drill down ดู cost วางแผนให้ดี querying / billing / automation (Scripting, Azure Policy)
- Cost Saving
- Reservations จองยาว / Azure Hybrid Benefits เอา License On-Premise มาใช้ / Azure Credits / Azure regions แต่ละทีราคาไมใเท่ากัน
- Budgets / Pricing Calculator คิด Plan Cost ตาม Scenario
- Configure subscriptions : Knowledge check
Configure Azure Policy
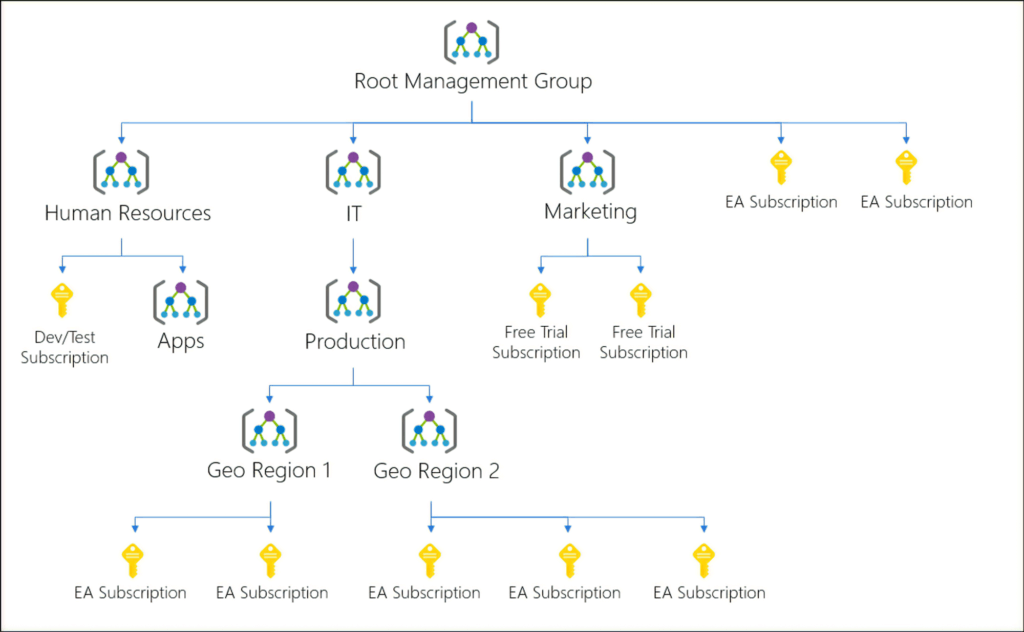
- Azure Policy มา Apply ที่ m/anagement groups level โดยสิ่งที่ต้องดู
- custom hierarchies and groups ได้ลึก 6 level ยิ่งลึกจัดการลำบาก ปรับให้เหมาะสมกับ Apply Policy + Cost Management
- policy inheritance + compliance rules
- cost reporting
- Implement Azure policies เข้ามาจุดดี ดังนี้ Enforce rules and compliance / Apply policies at scale / Perform remediation (อะไรที่ไม่เข้าพวกมันแนะนำ) / Exercise governance โดยงานอะไรบ้างที่เอา Policy มาใช้ อาทิ เช่น
- deployable resources (อะไรที่ใช้งานได้)
- location restrictions (ใช้งานได้ที่ไหน)
- rules enforcement (required อื่นๆให้จัดการไปในทางเดียวกัน เช่น บังตับใส่ tags)
- inventory audits
- Create Azure policies
- Step 1: Create policy definitions เอาจาก built-in policy หรือ import จาก GitHub ตัวอย่าง Policy เช่น Allowed virtual machine size SKUs / Allowed locations / disable public network access
- Step 2: Create an initiative definition เอา policy จาก Step1 มาจัดชุดให้เหมาะกับงานและ เช่น VM Prod ต้องมี
- Audit machines with insecure password security settings //Password Strong
- Configure Windows machines to run Azure Monitor Agent and associate them to a Data Collection Rule //เชื่่อม Monitor
- Network interfaces should not have public IPs //VM ต้องไม่เปิด Public IP
- Step 3: Scope the initiative definition - เอามาใช้ที่ไหน management groups, subscriptions, or resource groups
- Step 4: Determine compliance ตรวจสอบว่าตรงกับ Rule ไหม ต้องรอ 15 -30 นาที Apply และแจ้งผล โดยใน Wizard ที่สร้างสามารถกำหนด Remediation ได้ ถ้าไม่ตรง
- Configure Azure Policy: Lab
- Configure Azure Policy: Knowledge check
- Example Case: ตรวจสอบ/ป้องกัน การเปิด public ของ storage account ด้วย Azure Policy | by Sanchai Kongvijitpanit | Medium
Azure RBAC: Configure role-based access control
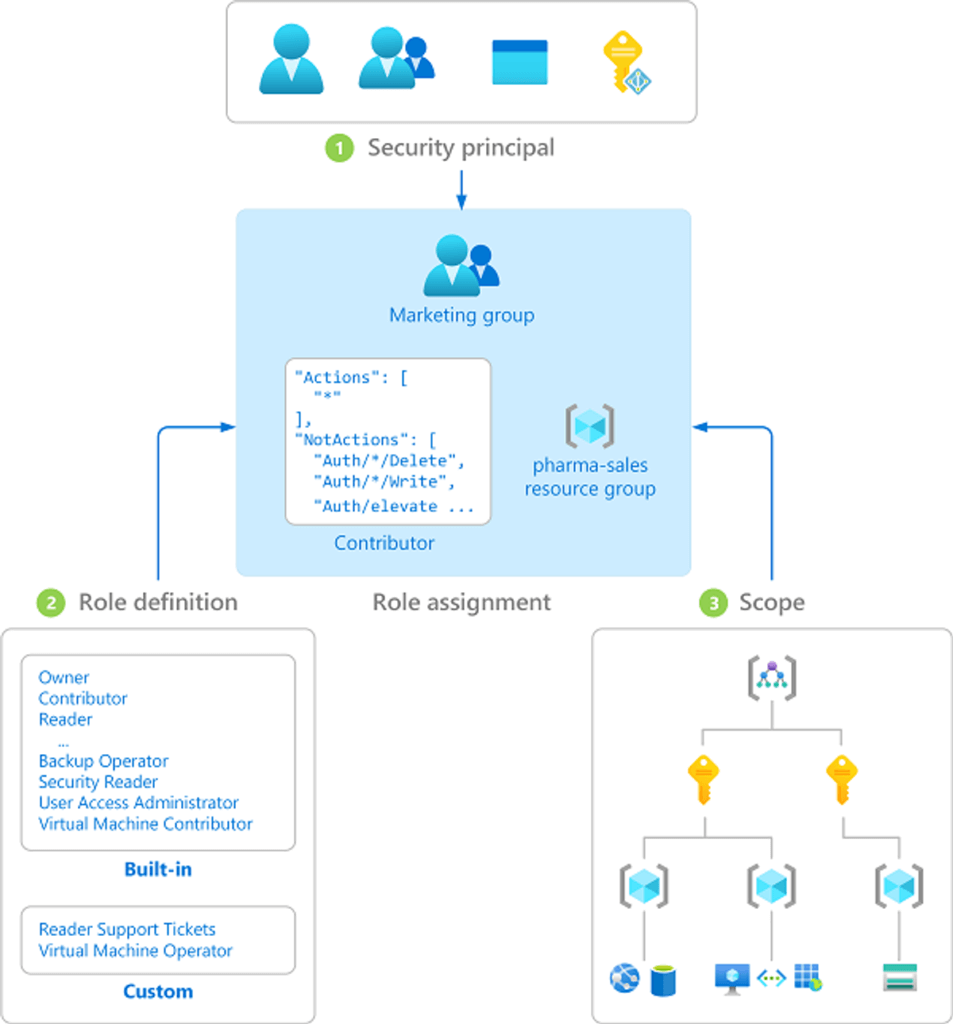
- Implement role-based access control
- Vocab
- Security principal ของแสดงสิทธิ User, group, service principal, managed identity
- Role definition สิ่งที่ทำได้ built-in พวก xxx Reader, xxx Contributor (create + manage แต่จัดการสิทธิ์ไม่ได้) , xxx Owner (Full + Delegate), User Access Administrator (จัดการบาง Resource ได้)
- Scope ทำได้แค่ไหน
- Assignment = Security principal + Role definition + Scope
- สิ่งที่ต้องดู
- requestors (ใครที่ขอมาใช้ resource //http request check)
- roles ดูจาก job responsibilities + work scenarios แล้วมาดูว่าจะเลือก built-in / custom definitions.
- scope of permissions ตาม requestor ในแต่ละ scenario
- Create a role definition - เป็น json บอกว่าอะไรทำได้ (Allow) / ทำไม่ได้ (Deny)
- Actions / NotActions / DataActions
- และ AssignableScopes (Role scopes) ตาม /subscriptions/<id> หรือ /subscriptions/<id>/<resource ..> / all "/"
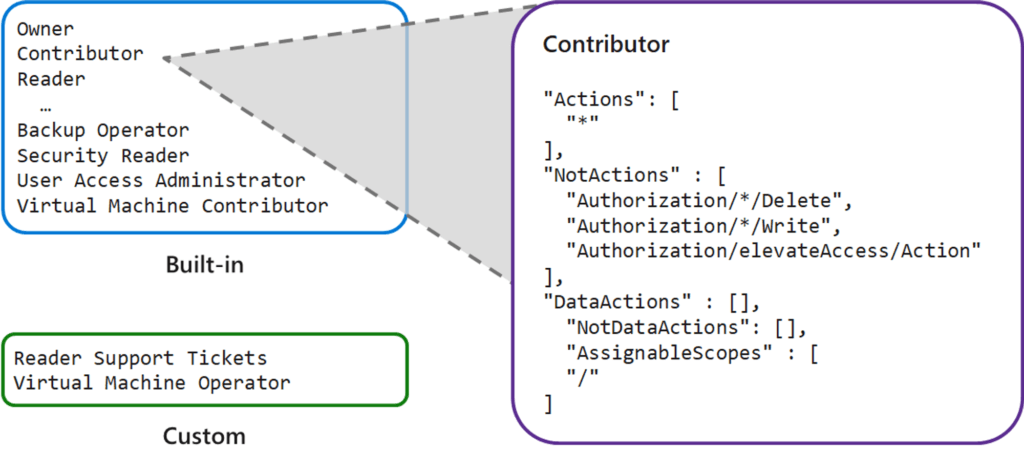
- ถ้าต้องใช้ Role มีอะไรต้องดูบ้าง
- using built-in roles ก่อน creating custom definitions ที่หลัง (Extend จากเดิม / ทำใหม่) และ The custom role definition also includes the scope of these permissions
- limiting access scope
- controlling changes to data เพื่อให้เกิด ACID + DCA
- applying to deny assignments

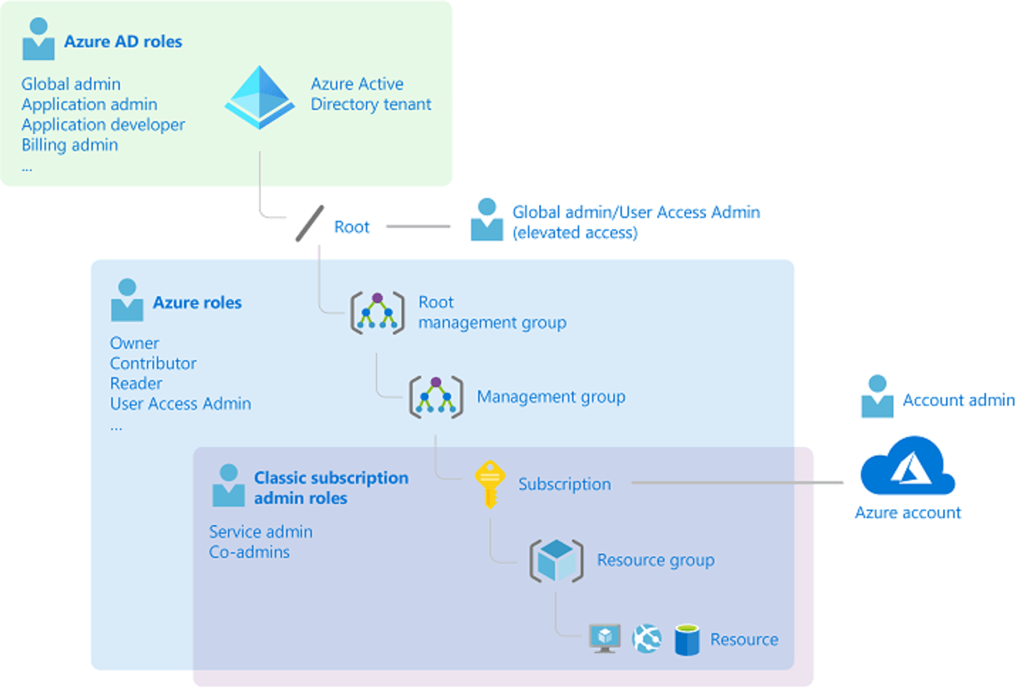
- Compare Azure roles to Azure Active Directory roles

- Apply role-based access control Azure AD (Authentication) / Azure RBAC (Authorize)

# ถ้า Script แบบนี้ ทำ json แล้ว Apply ไป New-AzRoleDefinition -InputFile C:\Temp\roleDefinition.json
Create Azure users and groups in Azure Active Directory
- Add user accounts
//Add //-CLI az ad user create //-PowerShell New-AzureADUser //Delete user accounts //-CLI az ad user delete. //-PowerShell Remove-AzADUser
- Bulk Create
$invitations = import-csv c:\bulkinvite\invitations.csv
$messageInfo = New-Object Microsoft.Open.MSGraph.Model.InvitedUserMessageInfo
$messageInfo.customizedMessageBody = "Hello. You are invited to the Contoso organization."
foreach ($email in $invitations)
{New-AzureADMSInvitation `
-InvitedUserEmailAddress $email.InvitedUserEmailAddress `
-InvitedUserDisplayName $email.Name `
-InviteRedirectUrl https://myapps.microsoft.com `
-InvitedUserMessageInfo $messageInfo `
-SendInvitationMessage $true
}
- What are user accounts in Azure Active Directory? (Knowledge Check)
- Exercise - Add and delete users in Azure Active Directory
- Access rights in Azure AD (Exercise - Assign users to Azure Active Directory groups)
- Direct assignment:
- Group assignment:
- Rule-based assignment: based on user or device properties
- Why use Azure AD B2B instead of federation?
- Azure AD B2B มัน Simple กว่า federation เอาเมล์มาใส่จบ Note: federation > you have a trust established with another organization (Other AD/Iam)
- Exercise - Give guest users access in Azure Active Directory B2B
Secure your Azure resources with Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC)
- Knowledge check - What is Azure RBAC?
- Exercise - List access using Azure RBAC and the Azure portal
- Exercise - Grant access using Azure RBAC and the Azure portal
- Exercise - View activity logs for Azure RBAC changes
- Knowledge check - Using Azure RBAC
Suppose a team member can't view resources in a resource group. Where would the administrator go to check the team member's access?
Ans Go to the resource group and select Access control (IAM) > Check Access.
Allow users to reset their password with Azure Active Directory self-service password reset
- Prerequisites
- License Premium P1 or P2
- Global Administrator privileges to set up SSPR + non-administrative user Test
- limit who you roll SSPR ด้วย
- How SSPR works
- STEP: Localization > Verification (Check it's a user and not a bot) > Authentication (Real User Security questions/ Security Code) > Password reset > Notification
- Authenticate a password reset
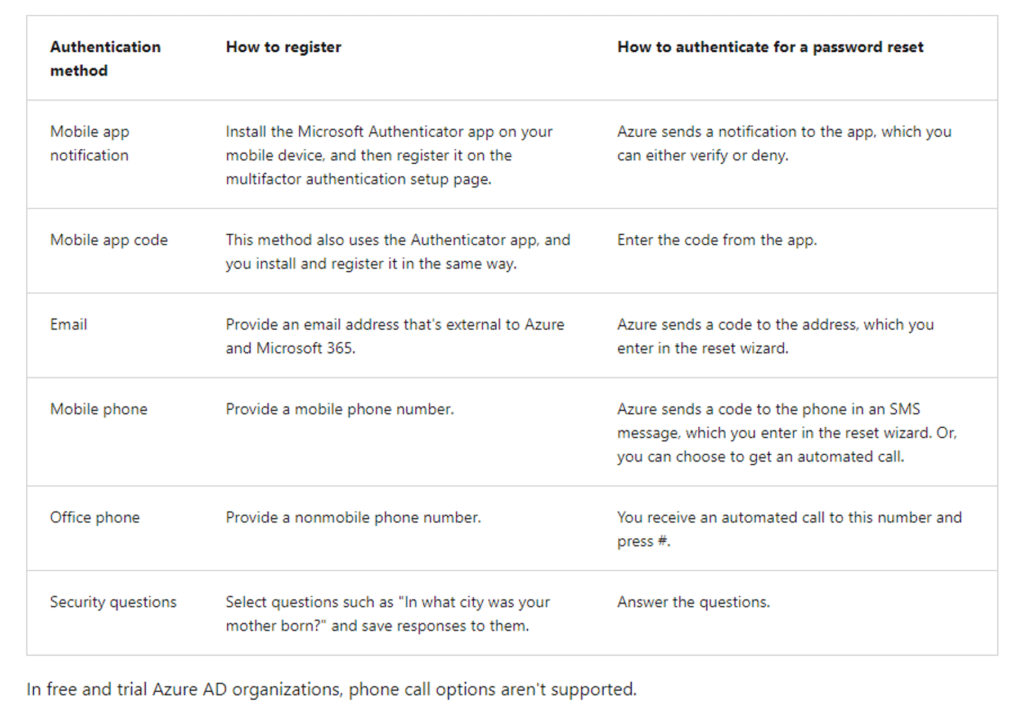
- Recommendations
- Enable two or more of the authentication reset request methods.
- Use the mobile app notification or code as the primary method, but also enable the email or office phone methods to support users without mobile devices.
- The mobile phone method ไม่แนะนำ มันเจอ send SMS fraud
- The security question option ไม่แนะนำ มันเดาง่าย
- administrator roles - A strong, two-method authentication policy is always applied
- notifications reset user แจ้งเจ้าของ / reset admin แจ้ง admin ทุกคน
- Scope of SSPR rollout: Disabled / Enabled / Selected (Test ก่อน Apply)
- Exercise - Set up self-service password reset
- Exercise - Customize directory branding
selecting Azure Active Directory > Manage, select Company branding > Configure.
Reference
Discover more from naiwaen@DebuggingSoft
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.