Table of Contents
Explore infrastructure as code and configuration management
- ทำไมต้อง infrastructure as code (IaC) ?
| Manual deployment | Infrastructure as code |
|---|---|
| Snowflake servers. Snowflake = unique configuration that cannot be reproduced (ทำซ้ำไม่ได้) โดยจะได้ตัว configuration drift | A consistent server between environments. |
| Deployment steps vary by environment. อันนี้จริง VM > Container ถึงเกิดมาแก้ปัญหานี้ | Environments are created or scaled easily configurations to be |
| More verification steps and more elaborate manual processes. จริง ตอนทำงานต้องตรวจ และจด Click + เยอะเหมือนกัน | Fully automated creation of environment Updates. ทำ Script มา Check ได้ |
| Increased documentation to account for differences. | Transition to immutable infrastructure. มันเป็น Code/Script Run ยังไง - ผลลัพธ์เหมือนเดิม - และ version-controlled ได้ |
| Deployment on weekends to allow time to recover from errors. | Use blue/green deployments. จากบทที่แล้ว วิธีนี้จะช่วยลด Downtime แต่ต้องมี Hardware ทำ Blue/Green นะ |
| Slower release cadence to minimize pain and long weekends. | Treat servers as cattle(โคขุน?), not pets. |
- ทำไมต้อง configuration as code ?
- คล้ายๆ infrastructure as code หลังๆก็ลด Bug / เพิ่ม Consistency / จัดการเวอร์ชันได้ง่าย / Deploy + Scale เร็ว
- imperative vs declarative configuration
- Declarative (functional) - what the final state should be //ไม่ Logic เขียนอะไรมา Run ๆได้อย่างนั้นเลย ไม่รู้ว่ามายังไง ทำไมต้องแบบนี้ (abstracts นั้นเอง) ตัวอย่างเช่น Azure Resource Manage Template
- Imperative (procedural) - how for the final state //มี Logic การตัดสินใจ เช่น IF-ELSE / FOR
- Note ไม่วิธีการไหนที่ดีที่สุดนะ
- idempotent configuration
- infrastructure as code - Run แบบไหนได้แบบนั้น เหมือน Math เช่น 1+1 = 2
- แต่ถ้าจะทำให้เป็น idempotent ถ้ามีแล้ว recreating / การจัดดารพวก Resource Name+ID
- Knowledge check: Explore infrastructure as code and configuration management
Create Azure resources using Azure Resource Manager templates
- Azure Resource Manager templates ดียังไง ?
- improve consistency
- express complex deployments (ทำให้มันง่าย และมีลำดับ) + reduce manual, error-prone tasks และเป็น Declarative รูปแบบ JSON
- reuse + modular และ linkable แทนที่จะทำ ARM ชุดใหญ่ๆ ก็มาทำที่ละ Sub System แทน
- Explore template components
- Parameters / Variables / Functions / Resources / Outputs
- Manage dependencies - ใช้คำสั่ง dependsOn เพื่อบอกว่าต้องรออะไรก่อน ทำงานชั้นต่อไป
- แต่ต้องระวัง Circular Reference
- Modularize templates
- Linked template แยกไฟล์ ARM Template เชื่อมด้วย Link
- Nested template รวมไฟล์ ARM Template ทำให้ทั้งหมดอยู่ไฟล์เดียว
- Deployments modes - best practice, one resource group per deployment.
- validate
- incremental mode (default)
- complete mode
- Securing an external template - ใช้ shared access signature (SAS) tokens
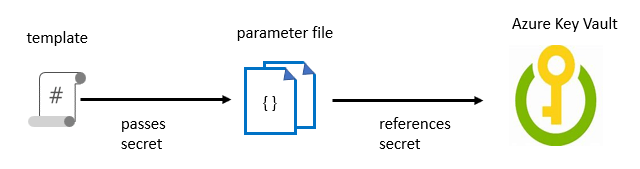
- Manage secrets in templates
- Reference Key Vault ID ในส่วน parameter ของ ARM Template
- ใน Azure Key Valut กำหนด enabledForTemplateDeployment=true
- Path นี้ผมว่ามันคล้าย [AZ-204] Implement infrastructure as a service solutions: Create and deploy Azure Resource Manager templates
- Lab 14: Azure deployments using Azure Resource Manager templates
- Knowledge check: Create Azure resources using Azure Resource Manager templates
Create Azure resources by using Azure CLI
- Azure CLI - เป็นชุดคำสั่งที่เอาไว้จัดการ resource บน Azure
- Interactive - เขียนยน Shell และ Execute ขึ้นมาเลย
- Scripted - ทำเป็นไฟล์ เอาไว้รันซ้ำได้
- ถ้าไม่รู้ Command คำสั่ง
az find <service / keyword>
หรือaz [groups] [subgroups] --help - รูปแบบของ Azure CLI จะแยกเป็น 2 กลุ่ม
- groups - สื่อถึง Service ของ Azure
- subgroups - คำสั่งที่ใช้ได้กับ Service นั้นๆ
- ตัวอย่าง เช่น Resource Group / VM
az group create --name <name> --location <location> az group list --output table az vm create -g MyResourceGroup -n MyVm --image MyImage az vm start -g MyResourceGroup -n MyVm az vm stop -g MyResourceGroup -n MyVm
- Exercise - Run templates using Azure CLI - ลองสร้าง VM
- Knowledge check: Create Azure resources by using Azure CLI
Explore Azure Automation with DevOps
- Azure Automation เป็น cloud-based automation service จัดการงาน Manual / ทำซ้ำบ่อยๆ และมี Workflows ของมัน เพื่อมาดู Infra ของ Azure หรือ เจ้าอื่นๆ (เห็น AWS) หรือ On-Premise ก็ได้ มองว่าเป็น Power Automate ของ Infra ก็ได้นะ
- Process automation
- Azure Automation State Configuration - PowerShell DSC << เอามา Monitor ว่าทุก Resouces Configuration ไปทางเดียวกันไหม ?
- Monitor + Update management
- Start and stop virtual machines (VMs)
- Manage Shared resources
- Run backups - ใน Non-DB เช่น BLOB
- การใช้งาน
- Create automation accounts
- สร้าง หรือ Import Run Book (จาก Run Book Gallery) โดยทำแบบ GUI / PowerShell / Python ก็ได้ ถ้าต้องการทำ Flow ดูตัวอย่างจาก Azure Automation (github.com)
- Run Book + Source Control Integration - สามารถเก็บ Script ไว้ใน GitHub / Azure DevOps (Git) / Azure DevOps (TFVC)
- Automation Shared Resources - ส่วนที่เอาไปใช้ในตัว Run Book ได้
- Webhook เป็นทางเลือกให้ Azure Automation ทำงานนอกเหนือจาก Schedule วิธีการนี้สามารถให้ Service อื่นๆ ของ Azure DevOps หรือ REST ใดๆมาใช้งานผ่าน Protocol HTTPS
- PowerShell Workflow - Runbook แบบ PowerShell จะเริ่มต้นด้วย Keyword WordFlow โดยใน Workflow Activity หลายๆอย่างข้างใน
workflow MyFirstRunbook-Workflow
{
ForEach -Parallel -ThrottleLimit 10 ($<item> in $<collection>)
{
<Activity1>
<Activity2>
}
<Activity3>
}
- Example PowerShell Workflow
workflow MyFirstRunbook-Workflow
{
Param(
[string]$VMName,
[string]$ResourceGroupName
)
....
#Task1: Start VM
Start-AzureRmVM -Name $VMName -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName
....
#Task2: copy file
$files = @("C:\LocalPath\File1.txt","C:\LocalPath\File2.txt","C:\LocalPath\File3.txt")
ForEach -Parallel -ThrottleLimit 10 ($File in $Files)
{
Copy-Item -Path $File -Destination \\NetworkPath
Write-Output "$File copied."
}
Write-Output "All files copied."
}
Implement Desired State Configuration (DSC)
- ปัญหา configuration drift เกิดจากตัว Environment เรามันไม่เหมือนเดิมจากที่เคย Initial ไว้ อาทิ เช่น Path ที่ลง App ไม่เหมือนเดิม (เคสนี้ส่วนตัวเจอจริงนะ ลูกค้า Deploy Tomcat ผิด path สรุปต้องใช้จน Server นั้น EOL เลย) หรือ Port เปลี่ยน
- ตรวจสอบ configuration drift
- ใช้ Azure Policy
- ใช้ Desired State Configuration (DSC) - ทำ Configuration มาตรวจสอบว่า Environment ยังเหมือนเดิมไหม ได้ทั้ง Windows และ Linux
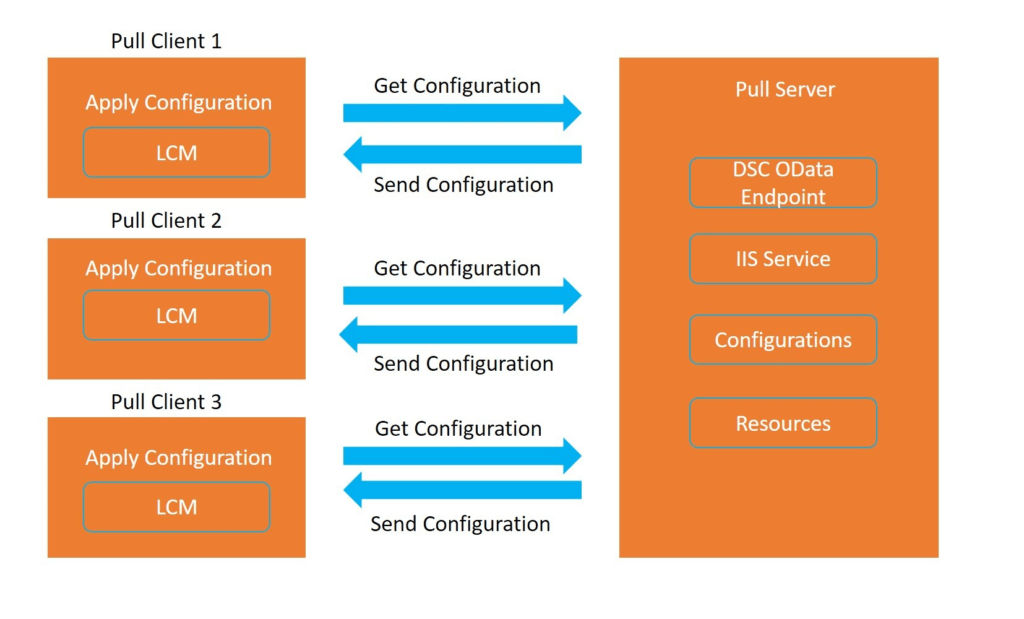
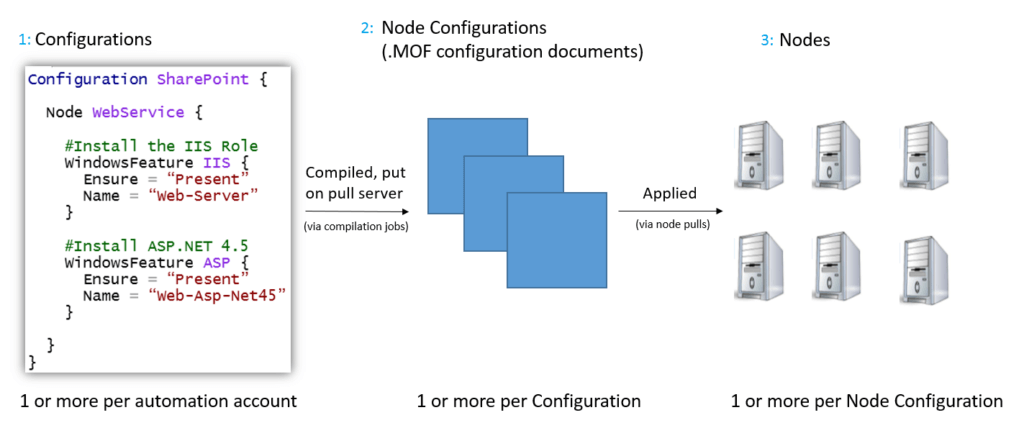
- Desired State Configuration (DSC) - components
- Configurations อยู่นอกสุด
- Node block กำหนดกลุ่ม Area ที่ต้องการตรวจสอบ
- Resources - configuration sets + properties สำหรับ resources / node นั้นๆ จากตัวอย่าง IIS/Bitlocker
- Local Configuration Manager (LCM) - runs on the nodes or machines you wish to configure
- Configurations อยู่นอกสุด
Configuration MyDscConfiguration
{
param
(
[string[]]$ComputerName='localhost'
)
Node $ComputerName
{
WindowsFeature IIS
{
Ensure = 'Present'
Name = 'Web-Server'
IncludeAllSubFeature = $true
}
WindowsFeature Bitlocker
{
Ensure = 'Present'
Name = 'Bitlocker'
}
}
}
MyDscConfiguration
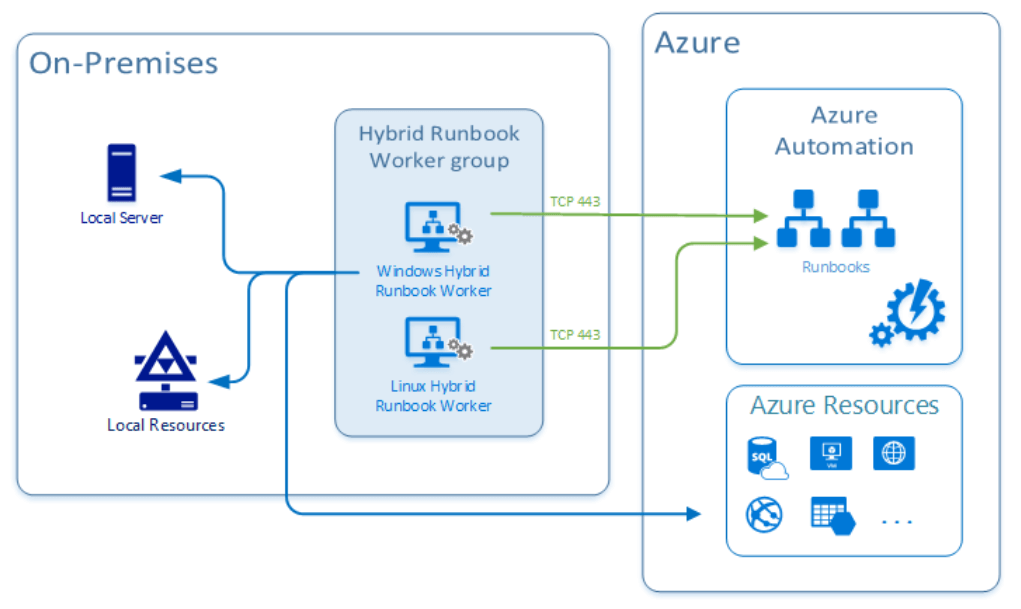
- Implementing DSC โดยจัดการจาก Azure Automation เพราะ มี Built-in pull server / DSC artifacts และ reporting data > Log Analytics โดยการจัดการ Node (Workload ที่สนใจ) มีรูปแบบ ดังนี้
- Push mode - User สั่งจากยิง DSC ไปยัง target node ทั้งที
- Pull mode - แต่ละ Node มาขอ DSC จาก Server กลาง
- สำหรับ hybrid management จะใช้ Azure Automation WebHook เข้ามาช่วย
- Exercise - Import and compile + Onboard machines for management
- Example [Azure] Azure Automation Step Note
- Knowledge check: Implement Desired State Configuration (DSC)
Implement Bicep
- Azure Bicep is the next revision of ARM templates
- Open-Source tool และเป็น domain-specific language (DSL)
- Install Bicep - มีทั้ง VS Code Extension และ CLI
- ใช้งานกับ Azure Pipelines / GitHub workflows
- Understand Bicep file structure and syntax
- Scope - resourceGroup (Default) / subscription / managementGroup / tenant
- Parameters
- Variables
- Resources - implicit dependency like a parent-child relationship. //location, name, and properties
- Modules - reusable templates
- Outputs
@minLength(3)
@maxLength(11)
param storagePrefix string
param storageSKU string = 'Standard_LRS'
param location string = resourceGroup().location
var uniqueStorageName = '${storagePrefix}${uniqueString(resourceGroup().id)}'
resource stg 'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts@2019-04-01' = {
name: uniqueStorageName
location: location
sku: {
name: storageSKU
}
kind: 'StorageV2'
properties: {
supportsHttpsTrafficOnly: true
}
resource service 'fileServices' = {
name: 'default'
resource share 'shares' = {
name: 'exampleshare'
}
}
}
module webModule './webApp.bicep' = {
name: 'webDeploy'
params: {
skuName: 'S1'
location: location
}
}
output storageEndpoint object = stg.properties.primaryEndpoints
- Knowledge check: Implement Bicep
Note:
- สำหรับ Azure SQL เวลา Deploy เค้าจะแนะนำให้ทำ DACPAC ที่มันจะมัดรวม schema changes + data.
Reference
Discover more from naiwaen@DebuggingSoft
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.