สำหรับ Course นี้ มีแนะนำมาอีกทีครับ เห็นว่าเหมือนแนสคิดเดียวกับ Udemy ครับ แต่ใน EDX แต่ละ Course เป็นอาจารย์จากมหาวิทยาลัยชั้นนำของโลกมาเปิดครับ โดยจุดแข็งที่ผมชอบฟรีครับ ถ้าอยากได้ใบ Cert ต้องจ่ายเงินครับ
หัวข้อที่เกี่ยวข้อง
- [MITx: 6.00.1x] Week 1: Intro to Python Primitive Data Type / if-else / IO / Function
- [MITx: 6.00.1x] Week 2: Approximate Solutions & Bisection Search + Problem Solving
- [MITx: 6.00.1x] Week 3: Structure Type / Side Effect
- [MITx: 6.00.1x] Week 4: Testing & Debugging & Assertion
- [MITx: 6.00.1x] Week 5: Type Hint / Lambda / Object Oriented Programming
- [MITx: 6.00.1x] Week 6: Algorithm + Big O
- [MITx: 6.00.1x] Week 7: Simple Plot
มาเข้าเรื่องของ Week แรกที่เรียนดีกว่าครับ เนื้อหานี้เป็นการปูพื้นฐานครับ โดยผมมองว่าคนไม่จบสายคอมเรียนได้นะครับ เค้าไม่ลงลึกจนเกินไป
📚Introduction
📚Knowledge Management
- Imperative knowledge = A recipe or “how-to” ซึ่ง Recipe ผมชอบคำนี้ อาจารย์เปรียบเปรยได้ดีเลยครับ จริงมัน คือ ขั้นตอนการทำงาน (Algorithm) ครับ
- Declarative knowledge = Statements of fact. เช่น ค่า PI = 3.14 / เก้าอี้มีสมุดสีแดงวางอยู่ เป็นต้น
📚Fixed & Stored Program
- Fixed Program - ทำงานเฉพาะอย่าง ทำมาเฉพาะเจาะจงให้ประมวลผลงานอย่างเดียว เช่น ทำมาเพื่อคิดเลข / ทำมาเพื่อคำนวณวิถีของจรวด (จริง น่าจะมองว่าเป็น SW ที่มาเจาะจงกับ HW)
- Stored Program - ทำได้หลายอย่างเลย แล้วแต่เราสั่งให้มันทำอะไร เอาง่ายๆ เราต้องเขียนโปรแกรมบอกเครื่อง
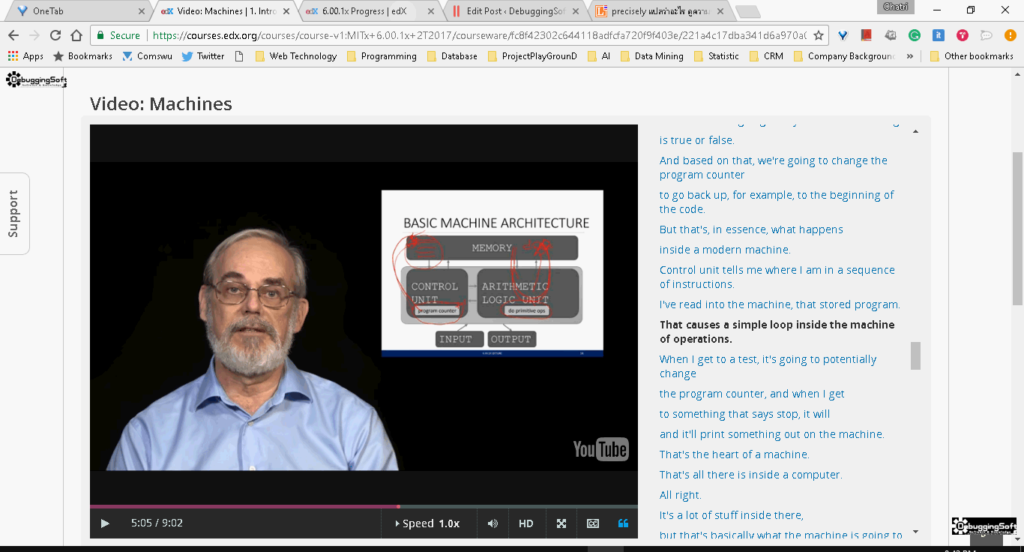
📚Basic Computer Architecture ตามรูปดีกว่าครับ
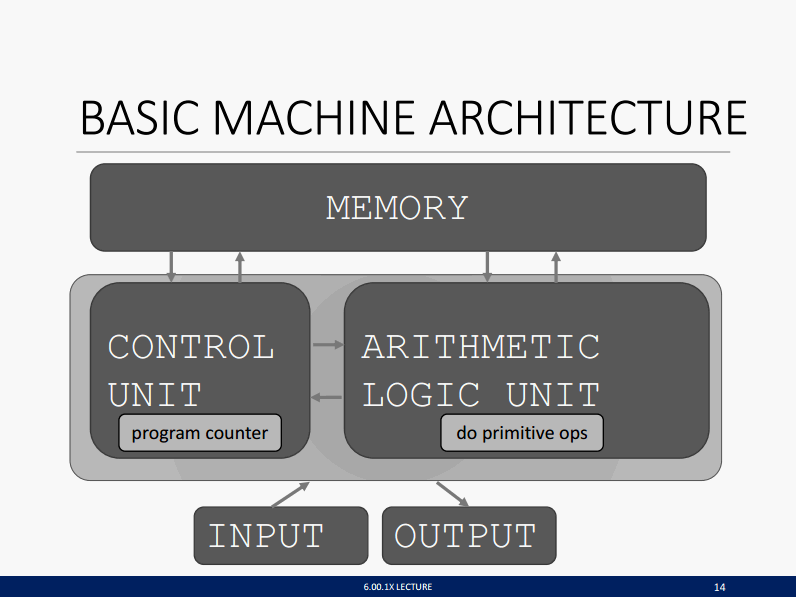
- A program counter The computer executes the instructions mostly in a linear sequence, except sometimes it jumps to a different place in the sequence.
Turing บอกถ้ามีการทำงานพื้นฐาน(Primitives Operation) เช่น การ Shift Bit/ AND / OR / NOT เป็นต้น เราสามารถประมวลทุกๆปัญหาได้บนโลก ถ้ามีปัญหาที่ต้องสร้าง Operation ใหม่ เราสามารถเพิ่มได้ โดยการทำ Abstract Data Type (เขียน Function ใหม่ และเรียกพวก Primitives Operation ด้านใน ถ้าใช้เครื่องเรียนพวก Assembly หรือ LC-3 ลองนึกดูว่า ถ้าต้องการหาเลขยกกำลัง มีขั้นตอนอะไรบ้าง)
📚Aspect of Language
- Syntax - ตรงตามโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน เเช่น ประโยคที่ดีควรมีประธาน + กริยา + กรรม
- Static Semantics - ตรงตามกฏเกณฑ์ ถ้าในภาษาอังกฤษ เป็นพวก Grammar ครับ ดู Syntax ว่าถูกตามกฏไหม
- Semantics - ดูความหมายและ ซึ่งบอกที่ประโยคเดียวกัน อาจจะตีความได้หลายแบบ แต่สำหรับ Computer ต้องตีความได้แบบเดียวเท่านั้นครับ
📚แนวคิดการคิดโปรแกรมภาษา Python หลักๆ มีเรื่อง
- Data Type - int, Boolean, float และ string (ตัวหลังเน้นเยอะเลย)
- Statement - คำสั่งต่างๆ
- Operation - การ + - * / และพวก Logic ต่างๆ อย่าง AND, OR
# MATH Operation print(5+2) print(5-2) print(5*2) print(5/2) print(5//2) # floor division print(5**2) print(10/3)
- String Method
# String is immutable
text = " a cat walks into a garden."
text.replace("cat ", "lion")
print(text) # a cat walks into a garden.
# =====================================
text = text.replace("cat", "lion")
print(text) # a lion walks into a garden. ที่เห็นว่ามันค่ามันเปลี่ยน เพราะมันแก้ Reference ใน Memory ให้เลย ง่ายๆสร้างใหม่นี่แหละ หลักการเต็มๆลองอ่าน Java และ C#
# ถ้าจะสร้าง String เลยใช้ slicer ตัวอย่าง แบบนี้ language = "C" + language[1:] print(language)
ตัวอย่างอื่น พบ Upper Lower ครับ
language = "Python" print(language.upper())
- Control Flow - IF-ELSE
# control flow
def grade(score):
if score >= 90:
return 'A'
elif score >= 80:
return 'B'
elif score >= 70:
return 'C'
else:
return 'Please retake exam !!!'
# กรณีที่ไม่ Return
# None pass
def sampleNone():
return None # special keyword
def samplePass():
pass- Iteration - พวก for while
# Define a list of numbers
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# Iterate over the list using a for loop
for number in numbers:
print("Current number:", number)
print("Loop finished")
# ===========================================
# ปกติพวก i++ ใน python ไม่มีใช้ range แทน
# Define the range of numbers
for i in range(5):
print("Current value of i:", i)
print("Loop finished")# while
# Initialize a counter
counter = 0
# Define the condition for the while loop
while counter < 5:
print("Counter value:", counter)
# Increment the counter
counter += 1
print("Loop finished")- Basic I/O - input กับ print
- Basic File
f = open("demofile.txt", "r")
print(f.readline()) # อ่านทั้งบรรทัด
print(f.readline()) # อ่านทั้งบรรทัด
f.close() # คืน Resource f = open("demofile2.txt", "a") # ค่าที่เป็นไปได้ x - create / a - append / w - write
f.write("Now the file has more content!")
f.close()
# open and read the file after the appending:
f = open("demofile2.txt", "r")
print(f.read()) สำหรับ csv ใช้ตัว import csv ใน python มีอยู่แล้วนะ มีการใช้ with เพื่อคุมการใช้ resource
# ====================================
# Read CSV
# ====================================
import csv
# Reading from a CSV file
with open('input.csv', mode='r') as file:
csv_reader = csv.reader(file)
# Skip the header row if there is one
next(csv_reader)
for row in csv_reader:
print(row)# ====================================
# Write CSV
# ====================================
import csv
# Data to write
data = [
['Name', 'Age', 'City'],
['Alice', 30, 'New York'],
['Bob', 25, 'Los Angeles'],
['Charlie', 35, 'Chicago']
]
# Writing to a CSV file
with open('output.csv', mode='w', newline='') as file:
csv_writer = csv.writer(file)
for row in data:
csv_writer.writerow(row)แต่จริงๆแล้ว ถ้าใช้พวก pandas จะง่ายกว่า และสั้นกว่าด้วยนะ มี Blog ด้วย ฮาวทู Pandas (กว่าจะได้มาเขียนอีกทีปี 2025 - ห่างจาก Blog นี้ไป 6-7 ปีเลย
- และอื่นๆ
📚สำหรับการเขียนโปรแกรม อันนี้เค้าให้ผ่านตัวเว็บ แต่ผมยังไม่ได้ลง 555
พยายามลองใช้ตัว Editor ที่ทำใน Term Proj ตอนเรียน ป โท ผมพบข้อจำกัดของ Editor ของ ตัวเองเยอะมากครับ พยายามลองงมๆ แก้ให้มันแก้ขัดไปก่อน แต่ก็มีปัญหาใหม่มาครับ โดยข้อจำกัดต่างๆ ผมมีเขียนสรุปไว้ ดังนี้
- ไม่มีหน้าจอ แบบ Interactive แนวพวก Command Line ครับ เวลาจะลองอะไร ต้องเขียน Code เต็ม Complile และ Run อีกทีครับ
- Code Format ปัญหาที่สำคัญของภาษา Python คือ การจัดเยื้ยง
- Syntax Check ยังขาดครับ บางอย่างมันควรรู้ตั้งแต่แรกครับ ไม่ใช่มารู้ผลเอาตอน Complie
- การ Bypass ค่าบางอย่าง เช่น โจทย์บอกว่าให้อ่านข้อมูลจากตัวแปร S โดยที่คุณไม่ต้อง initial ค่าอะไร ตัว Grader เป็นคนจัดการยัดค่าให้ และทดสอบกับ Test Case ครับ
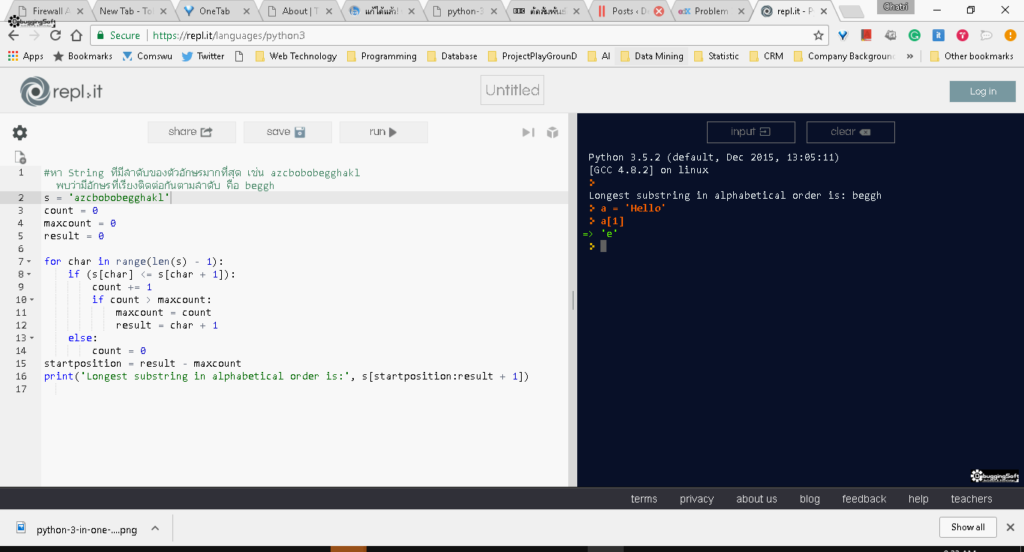
เลยใช้สลับกับ Online Editor ของ repl.it ครับ ผมว่ามันเจ๋งดี มีให้ตัว Debug กับตัว Command Line ให้ใช้ด้วย
📚Guess and Check
- Guess - ถ้ามองง่ายๆ มัน คือ การ Brute Force ครับ แต่พลังการคิดประมวลผลของเครื่องจักรมันทำได้ดีกว่าคนครับ
- Check - เอาตัว Recipe หรือ Algorithm มาช่วยตรวจสอบครับ
NOTE: หาเรารู้ Declarative Knowledge บางอย่าง เราสามารถทำให้โปรแกรมของเรา มีประสิทธิภาพ(Efficiency) มากขึ้นได้ครับ
สำหรับ Exercise ใน week แรกเยอะอยู่ครับ ผมใช้วิธีเปิด 2 จอ จอแรกเปิดโจทย์ สแกนไว้ก่อน อีกจอดู Video ครับ ถ้าคิดว่าอันไหนใช่ ก็ทำไปด้วยเลยครัย ส่วนตัว Problem Set จากที่ลองทำ ผมยอมรับว่าตกม้าตาย อะไรที่มันคิดว่าดูง่าย อย่างข้อที่ 1 และ 2 ผมทำแป๊บๆเสร์จ แต่ข้อสุดท้ายนี่และ ไปคิดเยอะ เสียเวลาไปต่อคำต้้งนาน พอได้ไปข้างนอก กินข้าว แล้วกลับมา จริงๆ เรานับจุด Start และ End จากนั้นนำมา subString ก็จบแล้ว ด้านล่างนี้เป็น Code ที่ผมเขียนปรับปรุงใหม่ครับ
#หา String ทีมีลำดับของตัวอักษรมากที่สุด เช่น azcbobobegghakl พบว่ามีอักษรที่เรียงติดต่อกันตามลำดับ คือ beggh
#ตัวแปร s ตัว Grader ทำหน้าที่ยัดค่ามาให้
count = 0
maxcount = 0
result = 0
for char in range(len(s) - 1):
if (s[char] <= s[char + 1]):
count += 1
if count > maxcount:
maxcount = count
result = char + 1
else:
count = 0
startposition = result - maxcount
print('Longest substring in alphabetical order is:', s[startposition:result + 1])ผมพยายามเขียน Blog ให้ได้ครบทุก Week นะครับ ตอนนี้ขอตัวไปลงตัว Anaconda ก่อน ถ้าใครสนใจลองตามมาเลยครับ MITx's 6.00.1x! Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Using Python
Discover more from naiwaen@DebuggingSoft
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.