This blog post is a How-To guide based on what I've learned from various sources and my experience trying MCP. If you're using .NET and have existing code that you want to convert into an MCP Server, what steps do you need to take? Let's dive in and find out.
For Thai Version: มาลองปรับ Code .NET(REST API) เดิมเป็น MCP Server
Table of Contents
What is MCP?
MCP, or Model Context Protocol, is a universal standard designed to extend the capabilities of AI Models (LLMs). This addresses the inherent limitations of models, which have finite knowledge and can sometimes hallucinate information.
Prior to MCP, integrating custom tools/services with LLMs required writing connection code specific to each AI provider's requirements or library specifications. Switching between models—from GPT to Claude to Qwen, for example—would be a major headache!
MCP solves this by establishing a universal standard that simplifies connectivity for everyone, which AI Models (LLMs) can then implement. Before using MCP, the first consideration is
Select a Model with Function/Tools Calling capabilities
Once AI Models (LLMs) can recognize tools, they can address knowledge limitations and reduce hallucinations. Examples include:
🔴 Time Management - Models don't have internal clocks; they only know dates from training data. Time-related tools enable AI to query and provide accurate responses.
🔴 Proprietary/Local Data - AI may not recognize what "Order 14334" refers to.
- Traditional approach: AI hallucinates or responds "I don't know" (with good prompting)
- Modern approach: AI invokes our prepared function to fetch Order 14334 data
🔴 Calculations - AI can miscalculate formulas, but with prepared tools, AI executes calculations according to our defined formulas.
Remember to validate data before passing it to tools!
🔴 Environmental Actions - This gives AI the ability to interact with its environment—booking tickets, displaying information on screens, controlling motor rotation, etc.
How MCP Server Works
- Transport (Connection Methods)
🔴 Before diving into coding, it's essential to understand the MCP Server connection methods, as they directly impact how we integrate AI+APP.
🔴 We need to examine the differences between connection methods: stdio / StreamableHTTP / SSE (deprecated).
| Transport Type | stdio | StreamableHTTP | SSE (deprecated) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | - 2-way communication between processes by reading stdin/stdout from Pipe. - If you're interested in learning more about Pipe, check out the blog post. | - HTTP response streaming / chunked | - Server-Sent Events stream real-time, one-way updates over HTTP via persistent text/event-stream connection with automatic reconnect. |
| Support Data Type | text / binary | text | text / binary |
| Use Case | CLI/Local Ex. Claude Desktop / Gemini CLI | Web/API | Web/API (Legacy) |
| Latency | Lowest | Medium | High |
| Remote Access | No | Yes | Yes |
| Multi-Client | No | Yes | Yes |
Currently, there are mainly 2 choices: stdio (local) / StreamableHTTP (WebAPI)
- Context Type
🔴 MCP Server responses currently come in 3 different formats.
| Context Type | Description | Security Concern | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prompts (User-controlled) | - Interactive templates invoked by user choice - Recommended prompt from the MCP for use in different scenarios. | - validate prompt inputs /outputs prevent injection attacks - unauthorized access to resources. | Slash commands, menu options |
| Resources (Application-controlled) | - Contextual data attached and managed by the client such as formular / example / cache data | - Data must be encoded - Validate Trust URI - Access Control | File contents, git history |
| Tools (Model-controlled) | - Functions exposed to the LLM to take actions - Usually, this is what I do the most to help prevent AI hallucination. | - Validate + Sanitize Inputs - access controls - Rate Limit | API POST requests, file writing |
Converting Existing .NET Code to an MCP Server
🔴 Before getting started, let's set up a demo project. I'll be preparing an InvestmentAPI for this. Originally on dotnet9, I've just upgraded to the brand-new dotnet10. My WebAPI endpoints are configured as follows
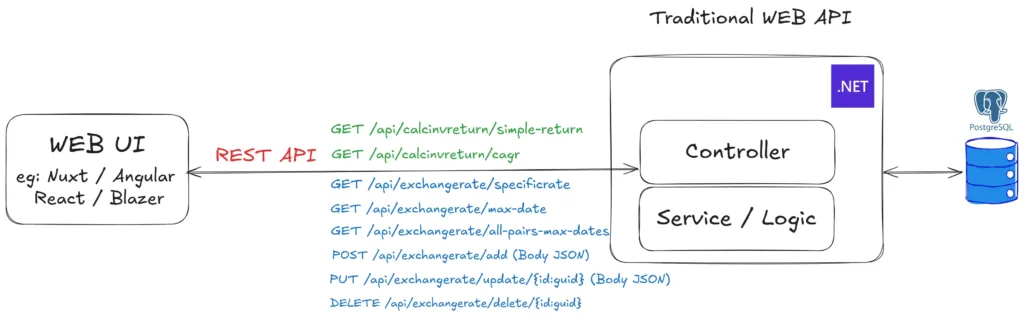
- CalcInvReturnController (Calculate Investment Returns)
- GET /api/calcinvreturn/simple-return
- GET /api/calcinvreturn/cagr คำนวณ CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) - ExchangeRateController (Exchange Rate)
- GET /api/exchangerate/specificrate
- GET /api/exchangerate/max-date
- GET /api/exchangerate/all-pairs-max-dates
- POST /api/exchangerate/add (Body JSON)
- PUT /api/exchangerate/update/{id:guid} (Body JSON)
- DELETE /api/exchangerate/delete/{id:guid}
🔴 Install NuGet Package ModelContextProtocol (App) / ModelContextProtocol.AspNetCore (WebAPI)
# stdio(local) dotnet add package ModelContextProtocol --prerelease # Or StreamableHTTP (WebAPI) / SSE dotnet add package ModelContextProtocol.AspNetCore --prereleas
🔴 In Program.cs, add the following code to configure it as an MCP Server:
- STDIO Configuration Details:
- AddMcpServer - Enables MCP Server functionality
- WithStdioServerTransport - Configures STDIO (Standard IO) transport
- WithPromptsFromAssembly / WithResourcesFromAssembly / WithToolsFromAssembly - Automatically discovers and registers classes and methods decorated with specific attributes as Prompts, Resources, or Tools
public class Program
{
private static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = Host.CreateEmptyApplicationBuilder(settings: null);
...
builder.Services
.AddMcpServer()
.WithStdioServerTransport()
.WithPromptsFromAssembly()
.WithResourcesFromAssembly()
.WithToolsFromAssembly();
// Register services
builder.Services.AddHttpClient<ExchangeRateService>();
// ....
}- Streamable HTTP / SSE Configuration:
- AddMcpServer - Enables MCP Server functionality
- WithHttpTransport - Configures Streamable HTTP / SSE transport. Default endpoints:
🏍️ Streamable HTTP - basepath:port
🛵 SSE - basepath:port/sse
- WithPromptsFromAssembly / WithResourcesFromAssembly / WithToolsFromAssembly - Automatically discovers and registers classes and methods decorated with specific attributes as Prompts, Resources, or Tools
Important: You must also add app.MapMcp(); to expose the MCP endpoints
public class Program
{
private static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddOpenApi();
builder.Services.AddControllers();
builder.AddObservability();
// Add PostgreSQL DbContext
builder.Services.AddDbContext<InvestmentDbContext>(
options => options.UseNpgsql(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"))
);
builder.Services
.AddMcpServer()
.WithHttpTransport()
.WithPromptsFromAssembly()
.WithResourcesFromAssembly()
.WithToolsFromAssembly();
// Register services
builder.Services.AddHttpClient<ExchangeRateService>();
builder.Services.AddScoped<ExchangeRateService>();
builder.Services.AddScoped<CalcInvReturnService>();
var app = builder.Build();
// Automatically create or migrate the database
using (var scope = app.Services.CreateScope())
{
var dbContext = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<InvestmentDbContext>();
// Use EnsureCreated or Migrate
dbContext.Database.Migrate(); // Applies migrations
// dbContext.Database.EnsureCreated(); // Creates the database without migrations
}
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.MapOpenApi();
}
app.MapMcp();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
}
}🔴 Now that we've adapted our existing API code to be exposed as Tools / Resources / Prompts
- Tools
- Add the [McpServerToolType] attribute to the class header to designate it as a Tool. When .WithToolsFromAssembly() is called in the builder, it automatically discovers and registers these classes.
- Decorate your method with [McpServerTool] and provide a detailed description. The more comprehensive the description, the more effectively the LLM can invoke it:
- Name - What the LLM uses for interpretation
- Title - Human-readable description for clarity
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[Produces("application/json")]
[McpServerToolType]
public class CalcInvReturnController : ControllerBase
{
[McpServerTool(Name = "calc_cagr", Title = "Calculate Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)")]
[HttpGet("cagr")]
public IActionResult CAGR(double initialValue, double finalValue, int years)
{
try
{
//Service + Validate Logic
double result = _calcService.CalculateCAGR(initialValue, finalValue, years);
return Ok(new { CAGR = result });
}
catch (ArgumentException ex)
{
return BadRequest(ex.Message);
}
}
}- Resource
- Add the [McpServerResourceType] attribute to the class header to designate it as a Resource. When .WithResourcesFromAssembly() is called in the builder, it automatically discovers and registers these classes.
- Decorate your method with [McpServerResource] and provide a detailed description. The more comprehensive the description, the more effectively the LLM can invoke it:
- Name - How the LLM identifies the resource
- UriTemplate - The URL pattern the LLM uses to request data
- MimeType - The data format returned (e.g., Text or Json)
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[Produces("application/json")]
[McpServerResourceType]
public class CalcInvReturnController : ControllerBase
{
[McpServerResource(
UriTemplate = "api://calcinvreturn/formulas/{type}",
Name = "investment_calculation_formula",
MimeType = "text/plain"
)]
[Description("Returns the formula for simple return or CAGR as plain text")]
[HttpGet("formulas/{type}")]
public string GetCalculationFormula(string type)
{
if (type.ToLower() == "simple-return")
{
return "Simple Return Formula: (Final Value - Initial Value) / Initial Value";
}
else if (type.ToLower() == "cagr")
{
return "CAGR Formula: (Final Value / Initial Value)^(1 / Years) - 1";
}
else
{
return "Invalid type. Available: simple-return, cagr";
}
}
[McpServerResource(
UriTemplate = "api://calcinvreturn/examples/{type}",
Name = "investment_calculation_example",
MimeType = "application/json"
)]
[Description("Returns an example calculation for simple return or CAGR as JSON")]
[HttpGet("examples/{type}")]
public string GetCalculationExample(string type)
{
if (type.ToLower() == "simple-return")
{
var example = new
{
Type = "SimpleReturn",
InitialValue = 1000,
FinalValue = 1200,
Calculation = "(1200 - 1000) / 1000 = 0.2",
Result = 0.2
};
return JsonSerializer.Serialize(example);
}
else if (type.ToLower() == "cagr")
{
var example = new
{
Type = "CAGR",
InitialValue = 1000,
FinalValue = 1464.1,
Years = 5,
Calculation = "(1464.1 / 1000)^(1 / 5) - 1 ≈ 0.08",
Result = 0.08
};
return JsonSerializer.Serialize(example);
}
else
{
return JsonSerializer.Serialize(
new { Error = "Invalid type. Available: simple-return, cagr" }
);
}
}
}Note: In this case, I've designed it to provide formulas and calculation examples rather than performing calculations directly, making it more distinct from Tools. Though technically, you could implement it the same way as Tools—it really comes down to how you choose to code it.
- Prompt
- Add the [McpServerPromptType] attribute to the class header to designate it as a Prompt. When .WithPromptsFromAssembly() is called in the builder, it automatically discovers and registers these classes.
- Decorate your method with [McpServerPrompt] and provide a description.
For this case, I preparing Prompts for AI to use, helping create clearer questions and invoke Tools for actual calculations, or to assist after getting results. Examples include:
- GenerateInvestmentAdvicePrompt - Investment recommendations
- RiskAssessmentPrompt - Risk management, etc.
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[Produces("application/json")]
[McpServerPromptType]
public class CalcInvReturnController : ControllerBase
{
[McpServerPrompt(Name = "investment_advice_prompt"),Description("Generates investment advice based on CAGR")]
public string GenerateInvestmentAdvicePrompt(double cagr, int years)
{
return $"Based on a CAGR of {cagr:P2} over {years} years, consider diversifying your portfolio and consulting a financial advisor for long-term growth.";
}
[McpServerPrompt(Name = "risk_assessment_prompt"),Description("Provides a risk assessment prompt for investments")]
public string RiskAssessmentPrompt(string investmentType)
{
return $"Assess the risk for {investmentType} investments: Consider market volatility, historical returns, and your risk tolerance before investing.";
}
}💻 Complete Code Implementation + Architecture Overview 💻
At this point, our architecture looks like this: we've transformed a traditional REST API into an MCP Server. The code changes include:
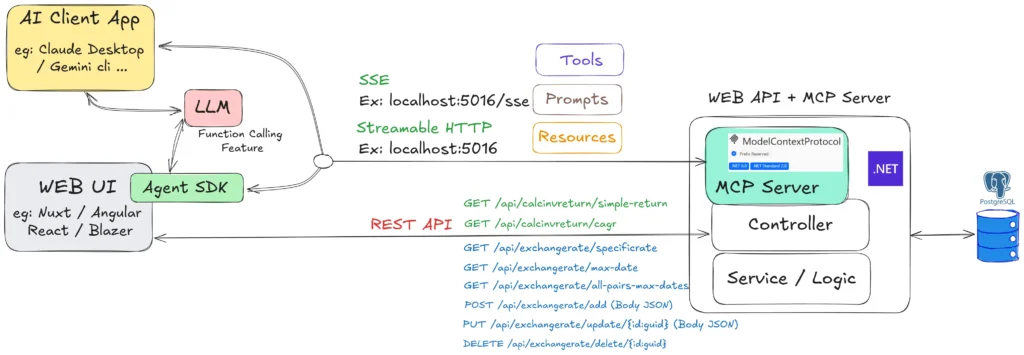
- Controllers converted to MCP Server: CalcInvReturnController.cs / ExchangeRateController.cs
- Program.cs updated to expose MCP Server endpoints
Next up is testing with the Inspector and Claude Desktop. We'll cover the Agent implementation in the next blog post! 😄
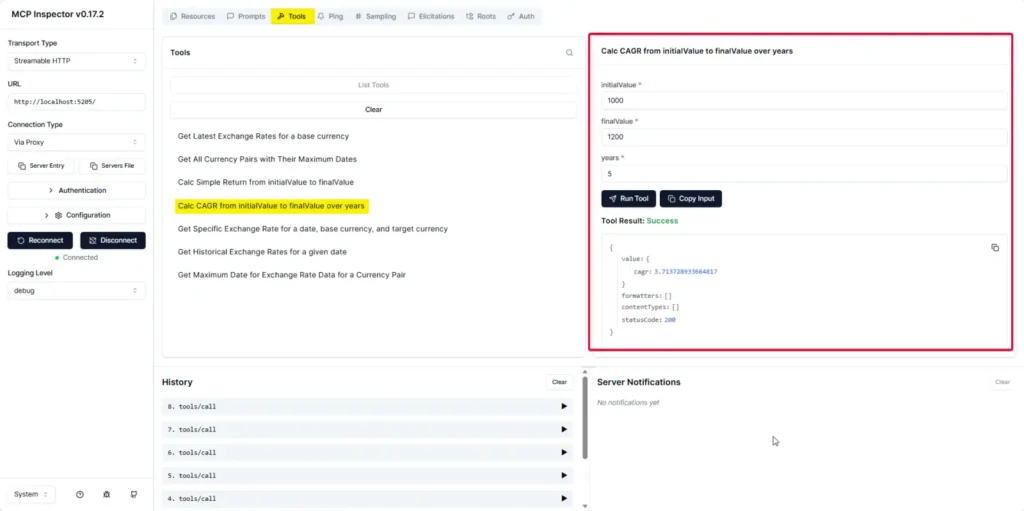
Testing MCP Server with MCP Inspector
Here, we'll use a tool called the MCP Inspector that displays all the available endpoints and features in our API.
🔴 Install modelcontextprotocol/inspector (Required Node.js: ^22.7.5)
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector
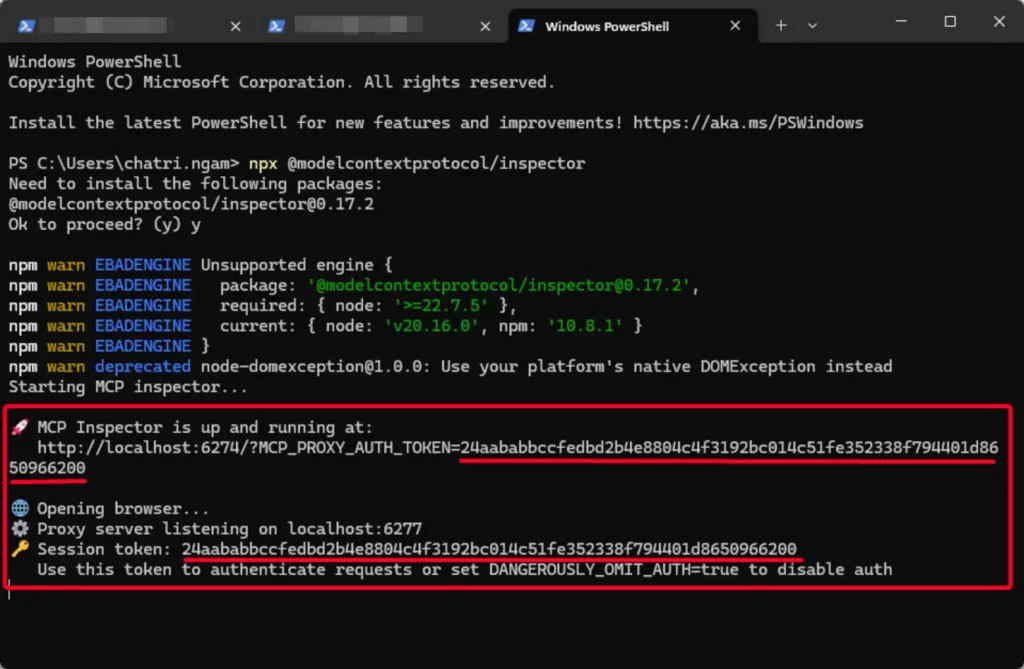
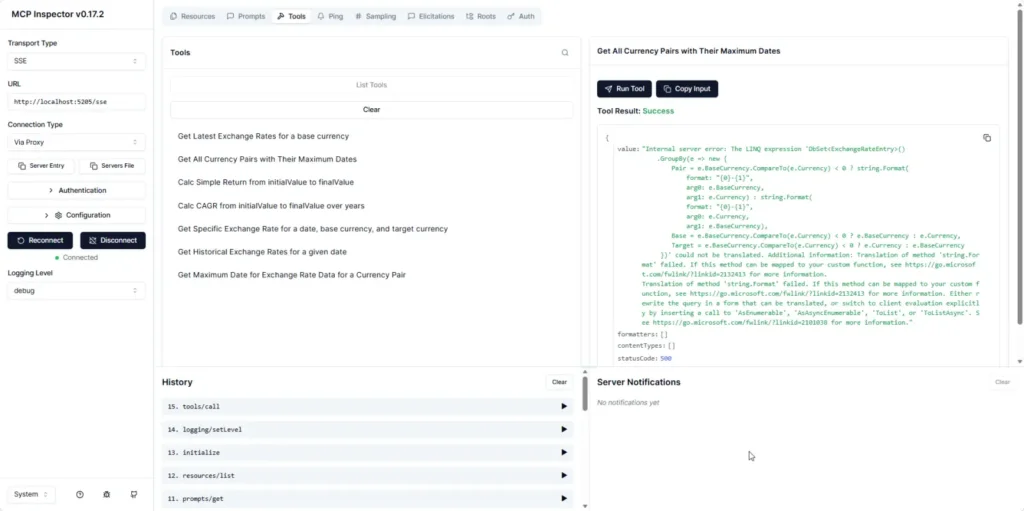
🔴 Then go to http://localhost:6274 — you'll find a tool there that lets you inspect/test our API. It shows all three MCP types: stdio, StreamableHTTP, and SSE. Testing feels similar to using Postman or a REST client. Error handling depends on how we write the code.
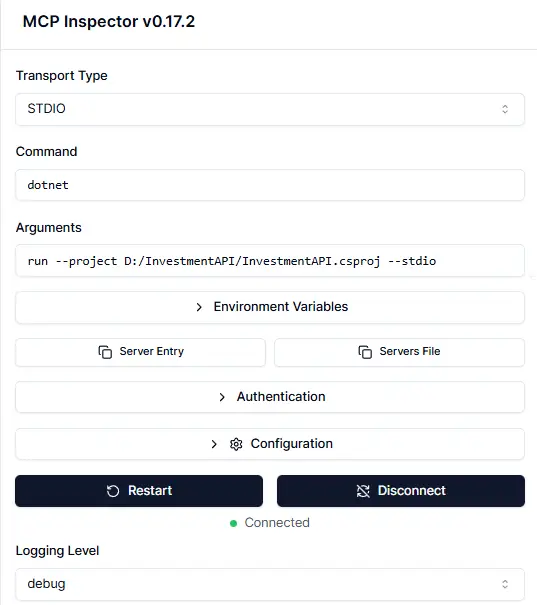
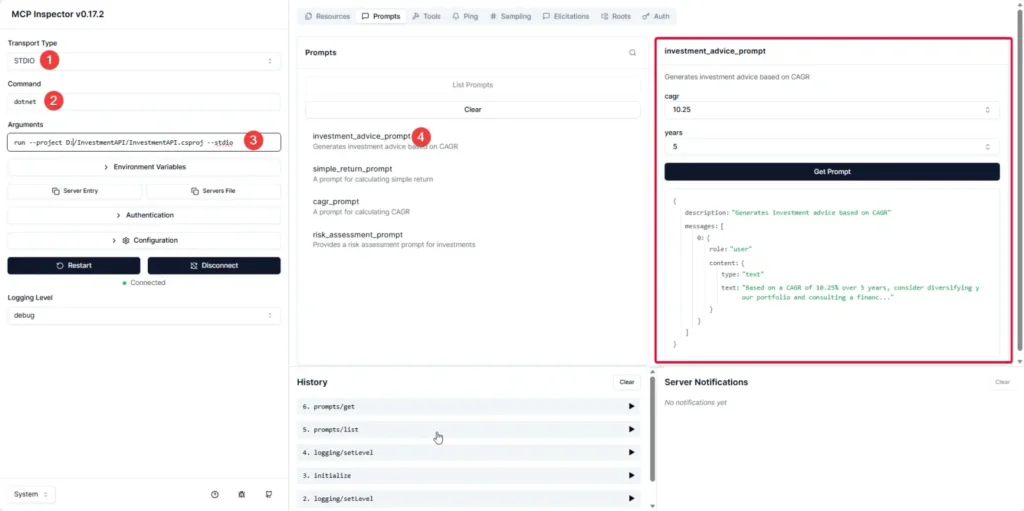
- STDIO
- When Start, try to adapt from the sample command to figure it out.
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector dotnet run --project PATH/TO/YOUR_MCP.csproj -- PARAM_IF_NEED npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector dotnet run --project D:/InvestmentAPI/InvestmentAPI.csproj -- --stdio
- There may be error cases, so be careful to add logging in the code.
Error from MCP server: SyntaxError: Unexpected token 'N', " Name: Syst"... is not valid JSON
at JSON.parse (<anonymous>)
at deserializeMessage (file:///C:/Users/Chatr/AppData/Local/npm-cache/_npx/5a9d879542beca3a/node_modules/@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/dist/esm/shared/stdio.js:26:44)
at ReadBuffer.readMessage (file:///C:/Users/Chatr/AppData/Local/npm-cache/_npx/5a9d879542beca3a/node_modules/@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/dist/esm/shared/stdio.js:19:16)
at StdioClientTransport.processReadBuffer (file:///C:/Users/Chatr/AppData/Local/npm-cache/_npx/5a9d879542beca3a/node_modules/@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/dist/esm/client/stdio.js:141:50) ...- In Tools, choose STDIO — after you click Connect you can view Tools / Resources / Prompt.
- SSE
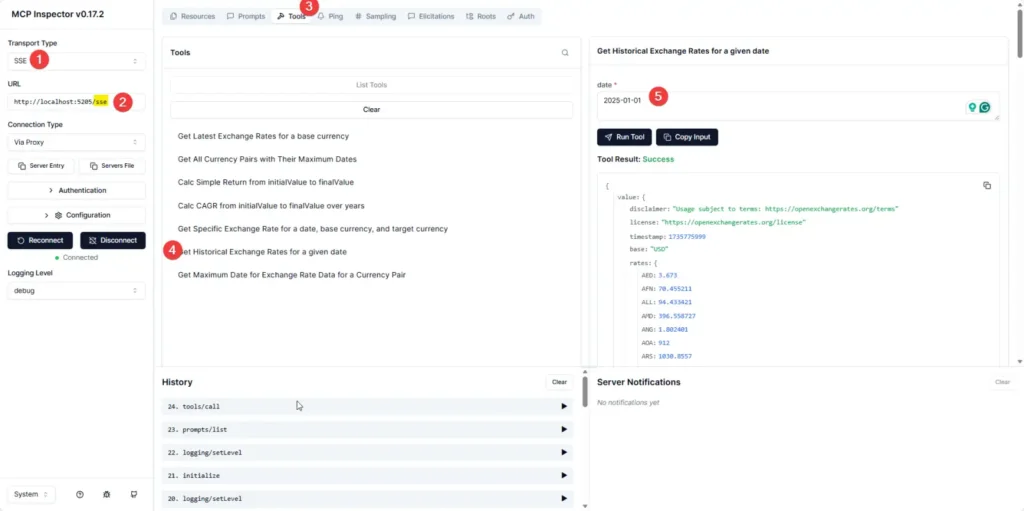
- Select SSE and set the path to [YOUR_IP]:[PORT]/sse.
- After you click Connect, open Tools → Resources → Prompt to inspect them.
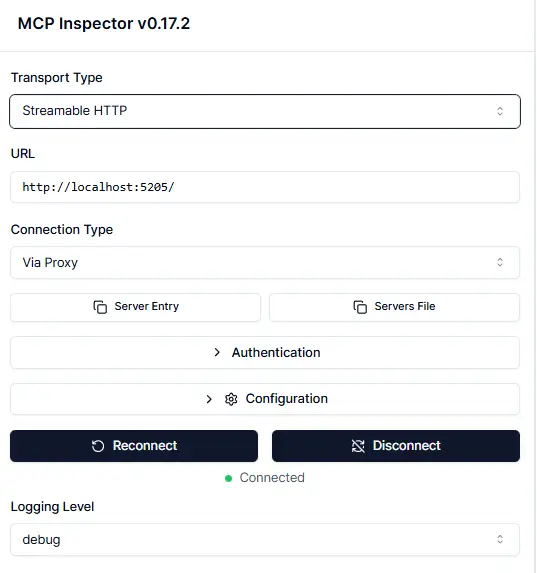
- Streamable HTTP
- Select Streamable HTTP and set the path to [YOUR_IP]:[PORT].
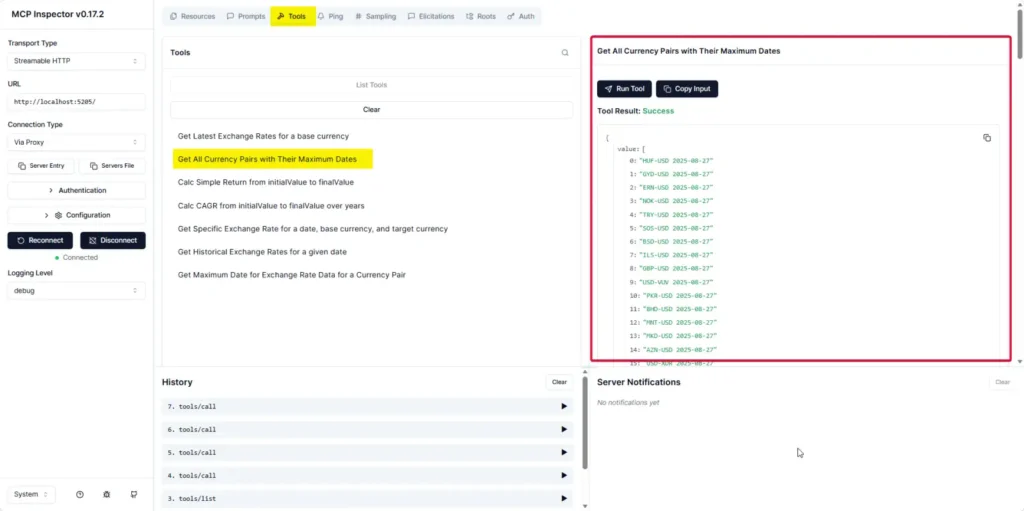
- After clicking Connect, open Tools — the interface shows both Pass and Fail cases (you should check how the code handles errors carefully).
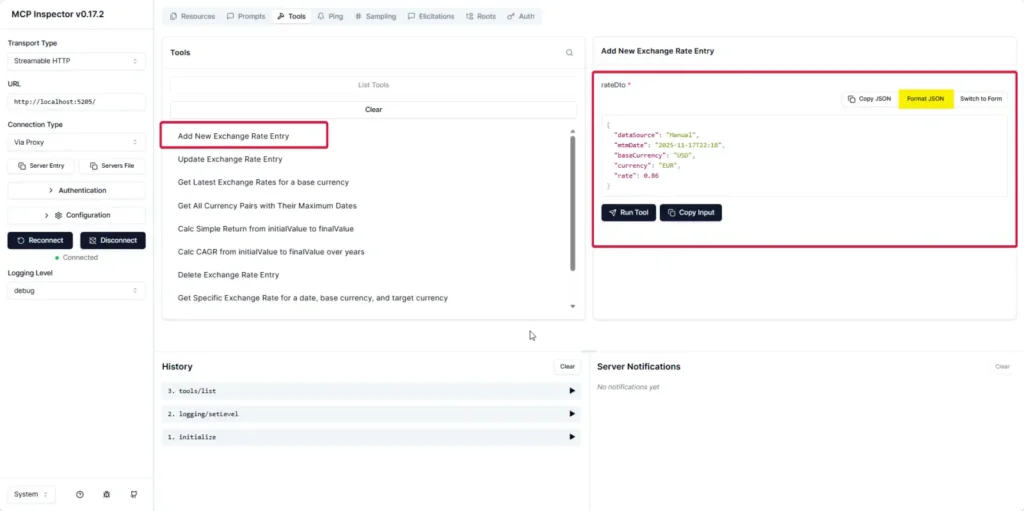
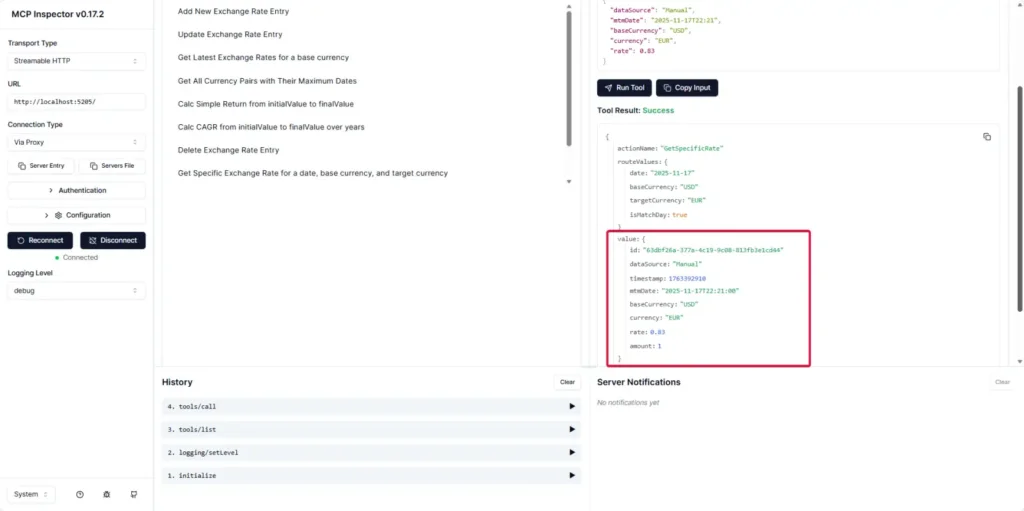
- In Tools, trying data operations (Add / Edit / Delete) also works: Add can be done via Form or JSON.
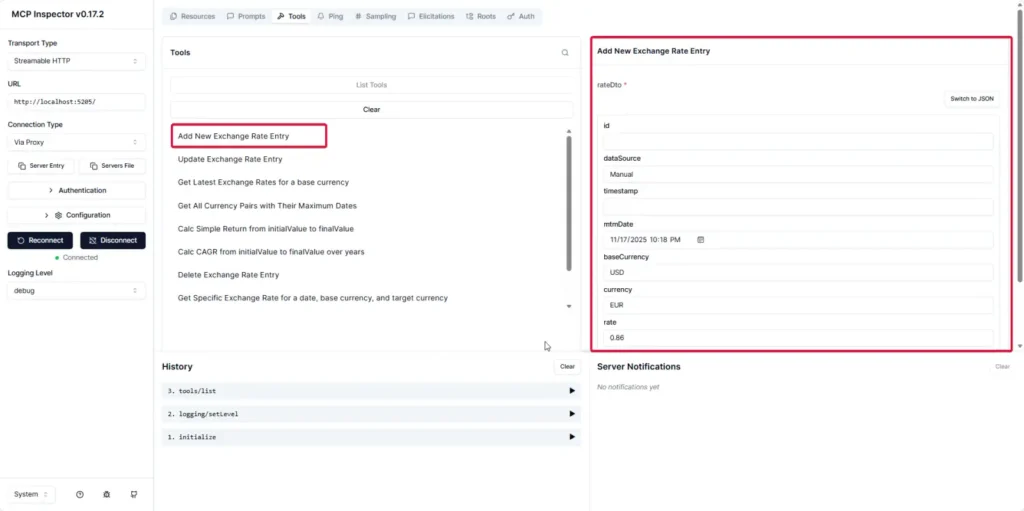
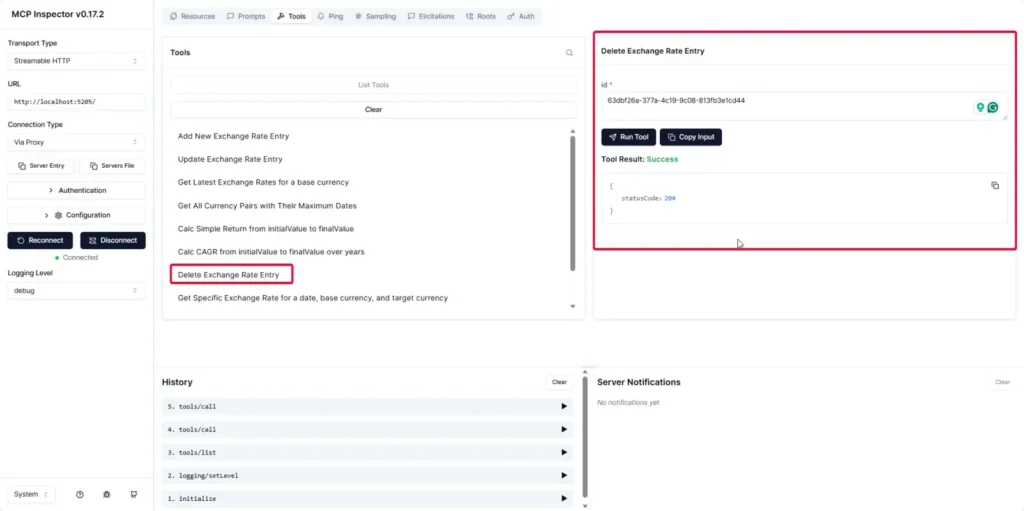
- Or Delete.
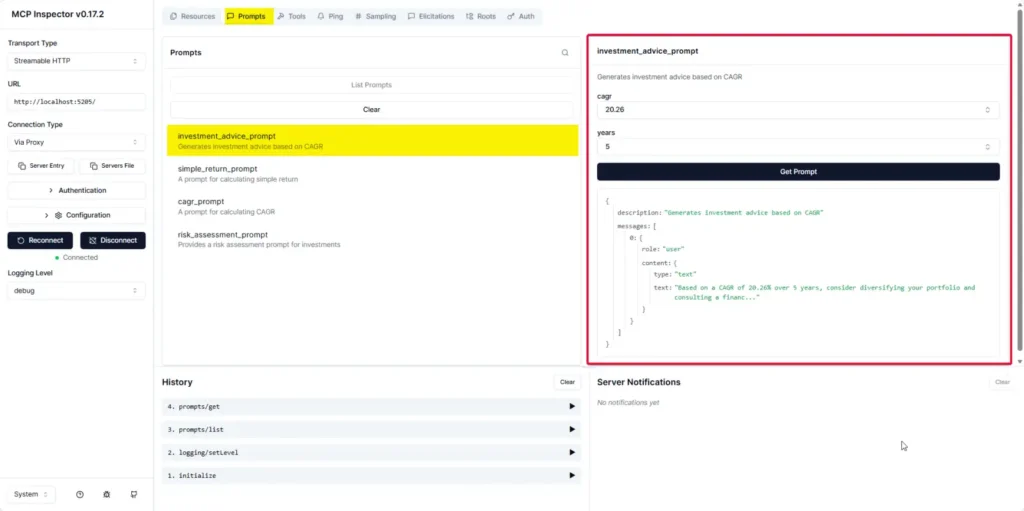
- Resources / Prompt.
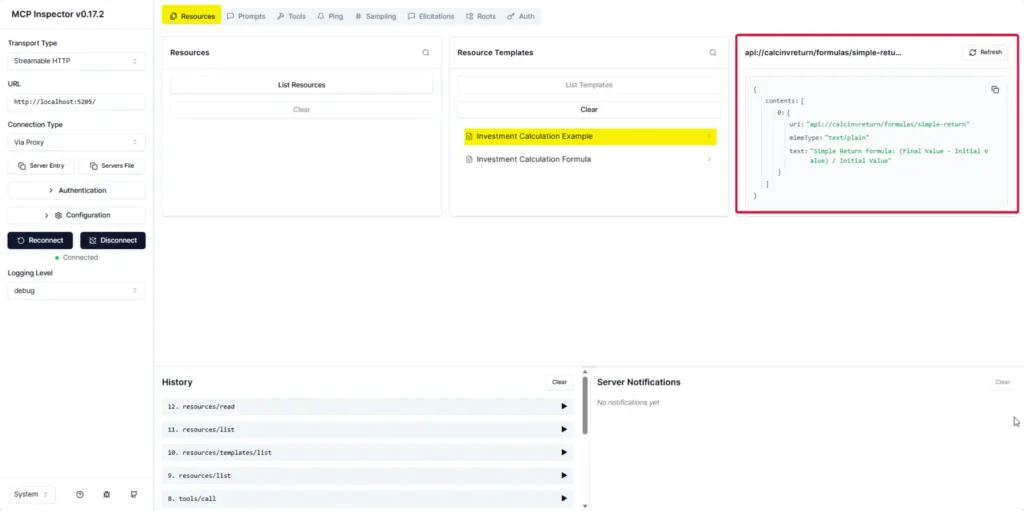
Source Code https://github.com/pingkunga/semantic-kernel-financial-plugin-sample/tree/feature/investapi
Test with Claude Desktop
📌 Before use, don't forget to check that MCP Tools Names have no spaces, otherwise there will be errors
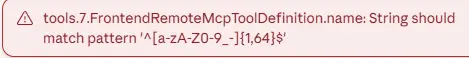
"tools.XXX.FrontendRemoteMcpToolDefinition.name: String should match pattern '^[a-zA-Z0-9_]{1,64}$'"📌 Solution > Just remove space use _

📌 Integration Step
- MCP server side -
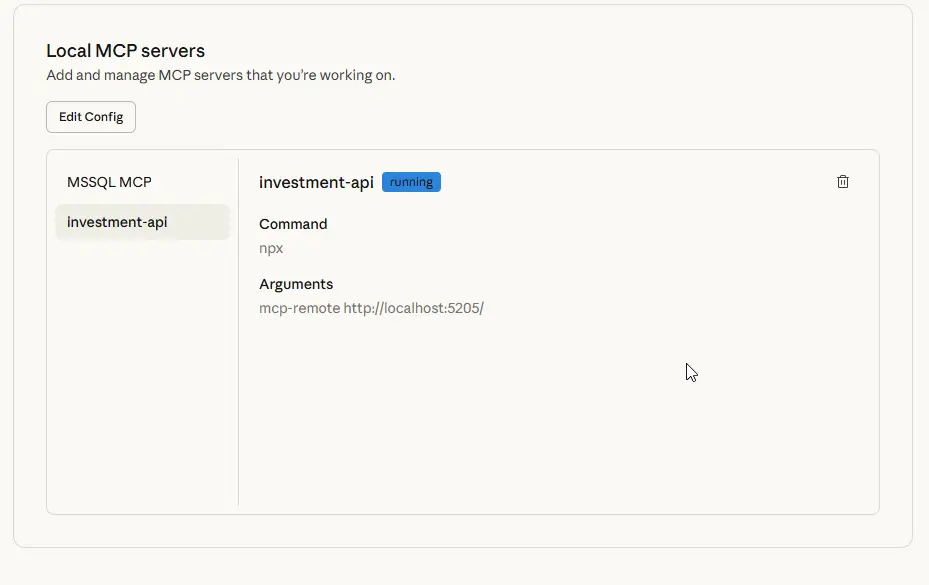
dotnet watch run - Claude side - You need to edit
claude_desktop_config.jsonin the path where Claude is installed to add our MCP server. For example, mine runs on http://localhost:5205/ and the "investment-api" part would be like this:
{
"mcpServers": {
"MSSQL MCP": {
"command": "D:\\NET_LAB\\SQL-AI-samples\\MssqlMcp\\dotnet\\MssqlMcp\\bin\\Debug\\net8.0\\MssqlMcp.exe",
"env": {
"CONNECTION_STRING": "Server=192.168.1.4,14330;Database=POSDB;User Id=Sample;Password=Sample;TrustServerCertificate=True"
}
},
"investment-api": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["mcp-remote", "http://localhost:5205/"]
}
}
}📌 Check MCP Tools already add in Claude Desktop or not !!
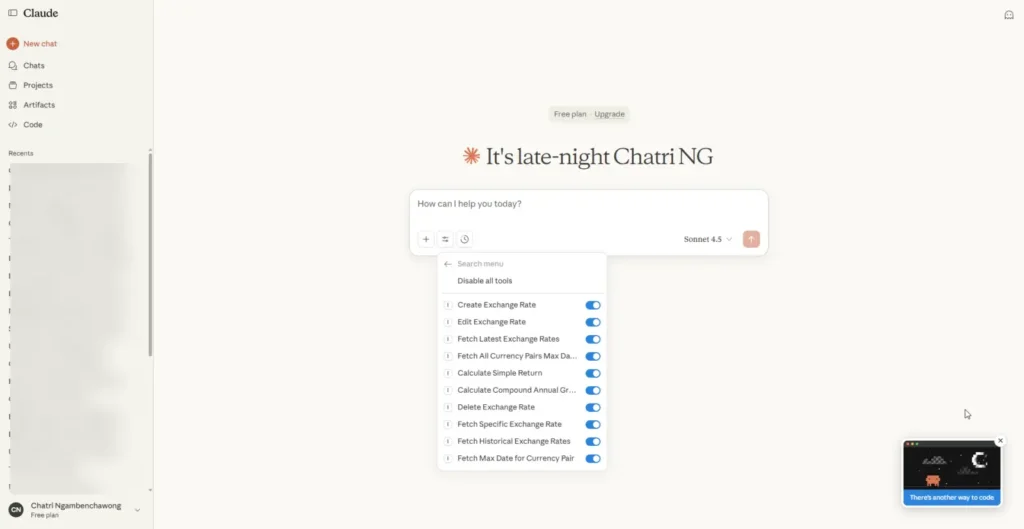
📌 Go ahead and try asking - it will call our MCP server, and check the JSON or server-side logs to see if it shows the call.
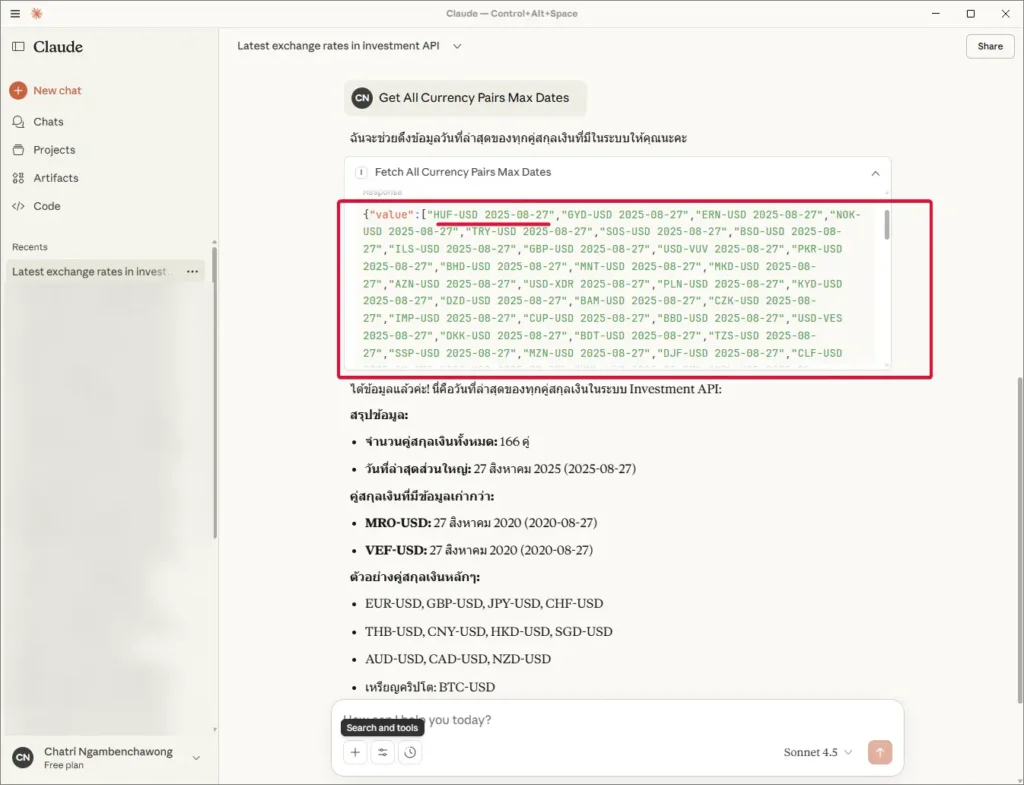
Next Step
🏯 After adding it to Claude Desktop, in the next blog post, I'll try using it with an Agent. Looking at the main project code, it still uses Semantic Kernel lol.
🎍 I'm thinking of switching to Microsoft Agent Framework, and I'll need to add more security features too. Right now, there's no API key - Opss.
Resource
- https://github.com/modelcontextprotocol/csharp-sdk/tree/main/samples
- https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/getting-started/intro
- Source Code https://github.com/pingkunga/semantic-kernel-financial-plugin-sample/tree/feature/investapi (I'm currently migrating to Microsoft Agent Framework)
Discover more from naiwaen@DebuggingSoft
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.