English Version: Back to Basic: Fundamental Data Structure in C# (English Version)
สำหรับ Blog นี้ ผมเขียนมาประกอบกับ Talk ที่ลองส่งในงาน .NET Developer Day 2025 - Thailand ครับ โดยแรงบันดาลใจในการเขียนเรื่องนี้ มาจากที่ว่าช่วงเดือนที่แล้วได้เข้าไปช่วยดับไฟ ในส่วนของ Performance Test ซึ่งมันเป็นในส่วน WEB API / WinApp ด้วย โดยสาเหตุที่ทำให้ Process มันช้า เกิดจากการเลือก Data Structure ที่ผิดประเภทมันมีหลายตัวนะ แต่ผมเจอแต่คนใช้ IList<T> / List<T> แทบจะทุกเรื่องเลย ถ้า Data มันเล็กๆมันจะไม่เห็นผลเท่าไหร่ แต่ถ้าข้อมูลมันเพิ่มจากหลักสิบ มาเป็นร้อย หมืน แสน ล้าน มันจะส่งผลได้ชัดเจนเลยครับ
ปัญหาที่พบ
- Component MoverBox มันตอบสนองช้ามาก เวลาเลือกข้อมูลจำนวนเยอะ
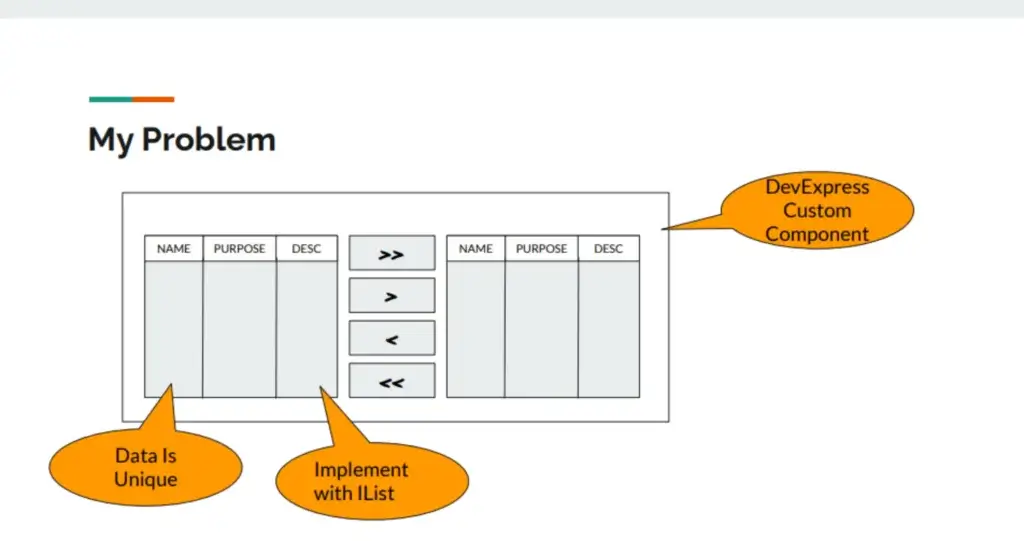
MoverBox ตัวที่ช่วยเลือกข้อมูลเยอะ โดยทำมาจาก DevExpress นี้แหละ มันอยู่มานานและน่าจะเกิน 10 ปีได้ โดยมี
- Grid Source / Grid Destination ซึ่ง User สามารถใช้ Feature ของ Grid Filter ข้อมูลได้
- มีปุ่ม >> / << เลือกทั้งหมดไปทาง Source / Destination
- มีปุ่ม > / < เลือกบางส่วน Source / Destination
- ข้อมูลใน Grid จะ Unique เสมอ
- สำหรับ Data Structure ที่ใช้จะเป็น List<T>
- Process ต่างๆ มันกินเวลามาขึ้น อย่างมีนัยสำคัญ เมื่อข้อมูลเพิ่มขึ้น
ใน Loop นอกจาก for แล้ว ยังมี Where หรือ FirstOrDefault หาใน List อีก ตัวอย่างจะประมาณนี้
public static void ProcessTransactionWithOnlyList(IList<TransactionDTO> pTransactions, IList<PortfolioDTO> pPortfolios, IList<PortPriceSouceDTO> pPortPriceSources)
{
// Iterate through transactions and find corresponding portfolio
foreach (var transaction in pTransactions)
{
// Use LINQ to find the portfolio with the matching PortfolioId
var portfolio = pPortfolios.FirstOrDefault(p => p.PortfolioId == transaction.PortfolioId);
if (portfolio != null)
{
// You can save or process the transaction with the portfolio here
//....
}
var portPriceSource = pPortPriceSources.FirstOrDefault(p => p.PortfolioId == transaction.PortfolioId);
if (portPriceSource != null)
{
// You can save or process the transaction with the portfolio here
//....
}
}
}Recap Data Structure
ไม่แน่ใจว่าคนอื่นเจอเหมือนกันไหม แต่ผมเจอคนที่ใช้ List แทน Data Structure ทุกอย่างเลย 55 มาทบทวนกันก่อน
- Data Structure + Big O คือ อะไร
สำหรับผม A way to organize a information to Add / Retrieve / Remove / Search efficiency เอาง่ายเป็นวิธีการจัดการข้อมูล มันมี Collection ที่ดีมาให้เลือก เราใช้ตาม use-case ที่เหมาะสมพอ โดยที่แต่ละ Operation Add / Retrieve / Remove / Search มันมีวิธีการวัด มันชื่อว่า Big O ไม่ต้องจำเยอะ จำสั้นๆ O(1) ดี แต่ถ้าแบบ O(n) หรือ O(n2) พวก Loop ซ้่อนกันหลายชั้น ไม่ดีแล้ว
- C# Data Structure
มันมีหลายตัว ตามรูปเลย
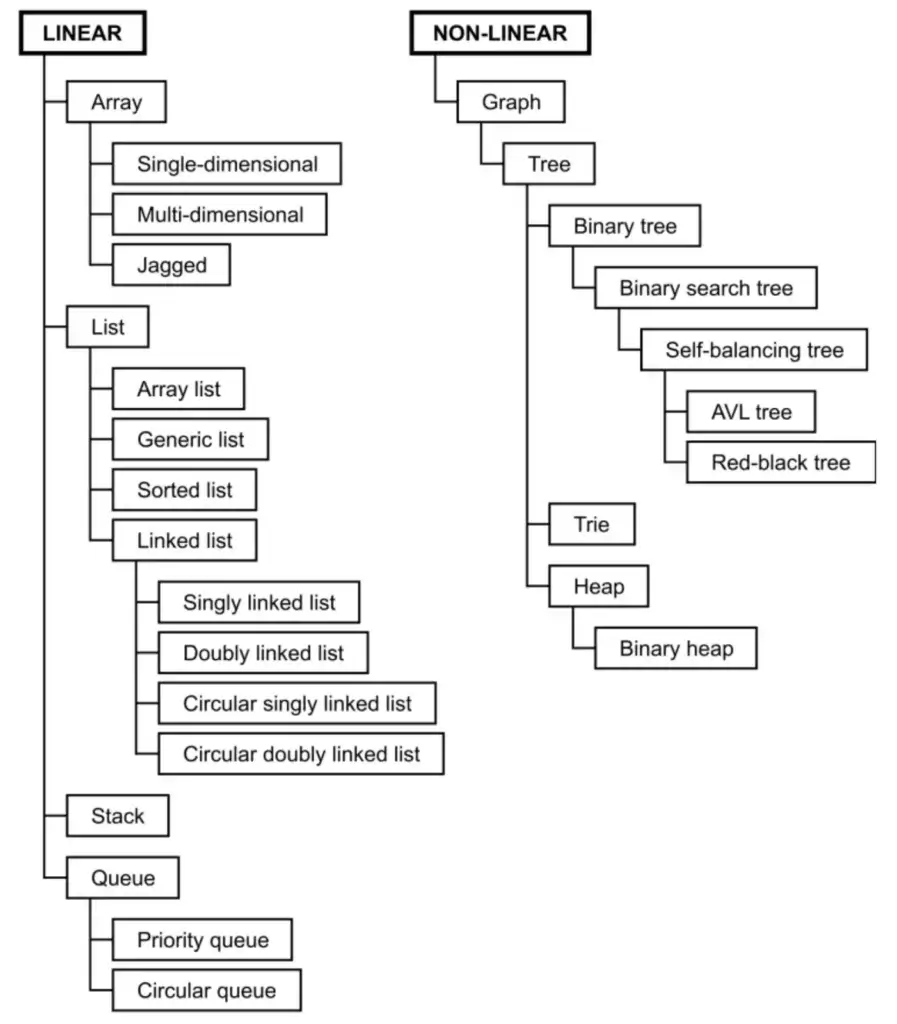
แต่เอาจริงเราใช้กันไม่หมดหรอก หลักผมใช้ List / Dictionary / Queue / HashSet ครับ
- Lists (List<T>)
Use Case:
- ใช้กรณีที่ต้องการเก็บต่อกันไป แต่เราไม่รู้ขนาด (dynamic size)
- Simple เอาไปใช้ได้หลายรูปแบบ
Note: Array Fixed Size
Big O Complexity:
- Access: O(1)
- Search: O(n)
- Insert: O(n) (O(1) if adding at the end)
- Delete: O(n)
Sample Code:
🚅 https://dotnetfiddle.net/CeShV4
🚅 https://dotnetfiddle.net/EN9v51 (C# Built-In InsertRange สำหรับแทรกกลาง)
- Dictionary<TKey, TValue>
Use Case:
- ใช้กรณีต้องการเก็บข้อมูลในรูปแบบ key / value เอา key มาของ
- Simple Caching / Lookup / Count Freq
Big O Complexity:
- Access: O(1)
- Search: O(1)
- Insert: O(1)
- Delete: O(1)
Sample Code:
🚅 https://dotnetfiddle.net/fjmgK1
จริงๆ ปัญหาที่เจอบ่อย การใช้ List แบบผิดๆ ใช้ list.where( x => x.yourkey) / list.FirstOrDefault( x => x.yourkey) อยากได้เป็นตัว Lookup ถ้าแปลงข้อมูลในอยู่รูปแบบ Dictionary (key / value) จะช่วยลด Cost จาก Search: O(n) > Search: O(1)
- HashSet<T>
Use Case:
- ใช้กรณีต้องการเก็บข้อมูลที่ไม่ซ้ำ (Unique) เช่น ต้องการข้อมูลใน Lookup ที่ไม่ซ้ำ
- การวัดว่าไม่ซ้ำ อย่าลืม implement Equals / GetHashCode
Big O Complexity:
- Access: O(1)
- Search: O(1)
- Insert: O(1)
- Delete: O(1)
Sample Code:
🚅 https://dotnetfiddle.net/KjkiPn
- Stack<T> & Queue<T>
Use Case:
- Stacks - ใช้ Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) เข้าก่อนออกที่หลัง ตัวอย่างที่ใช้
- การทำ Undo/Redo operation
- Syntaxes / Expression Parsing - check html tags - Queues ใช้ First-In-First-Out (FIFO) เข้าออกตามลำดับ ตัวอย่างที่ใช้
- Simple Message Queue
- Job scheduling with/without priority
Sample Code:
🚅 https://dotnetfiddle.net/5R2eAo (Stack)
🚅 https://dotnetfiddle.net/lPcTST (Queue)
Big O Complexity:
- Access: O(n)
- Search: O(n)
- Insert: O(1) Enqueue / Push
- Delete: O(1) Deque / Pop
อันนี้เขียนไปเป็นเพียงตัวอย่างนะ เพราะมันใน dotnet มันมี Data Structure หลายแบบเลย อาทิ เช่น
- System.Collections for Basic Type int string ….
- System.Collections.Generic for Generic Such as . Object / DTO
- System.Collections.Concurrent for multiple threads are accessing (Thread-Safe) พวก ConcurrentBag / ConcurrentDicionary / ConcurrentQueue เป็นต้น
สำหรับพวก Generic พวก DTO ต่างๆ อย่างลืมไป Implement Equals / GetHashCode ถ้าอยากรู้ว่ามัน คือ อะไรลองดูใน Blog นี้ได้นะ จะได้มีวิธีวัดว่าอะไรที่บอกวา่ Object นั้น Unique
แล้วแก้ไขยังไง ?
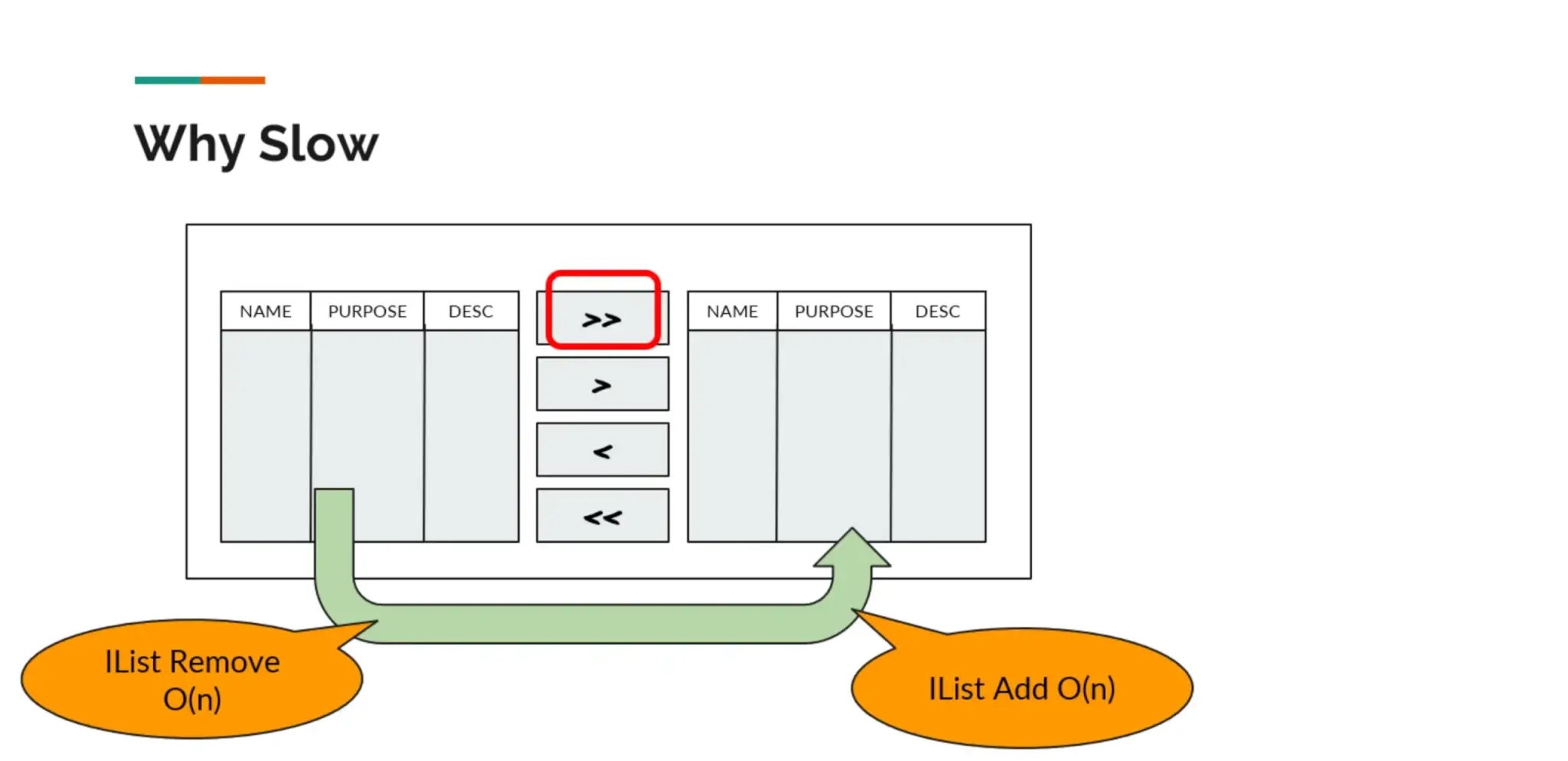
- Component MoverBox มันตอบสนองช้ามาก เวลาเลือกข้อมูลจำนวนเยอะ
จากเดิมใช้ IList<T> ในการเก็บข้อมูลฝั่ง Source / Desc เราเปลี่ยน Data Structure ที่ใช้งานเลยมาเป็น HashSet<T> เพราะข้อมูลใน MoverBox มัน Unique อยู่แล้ว
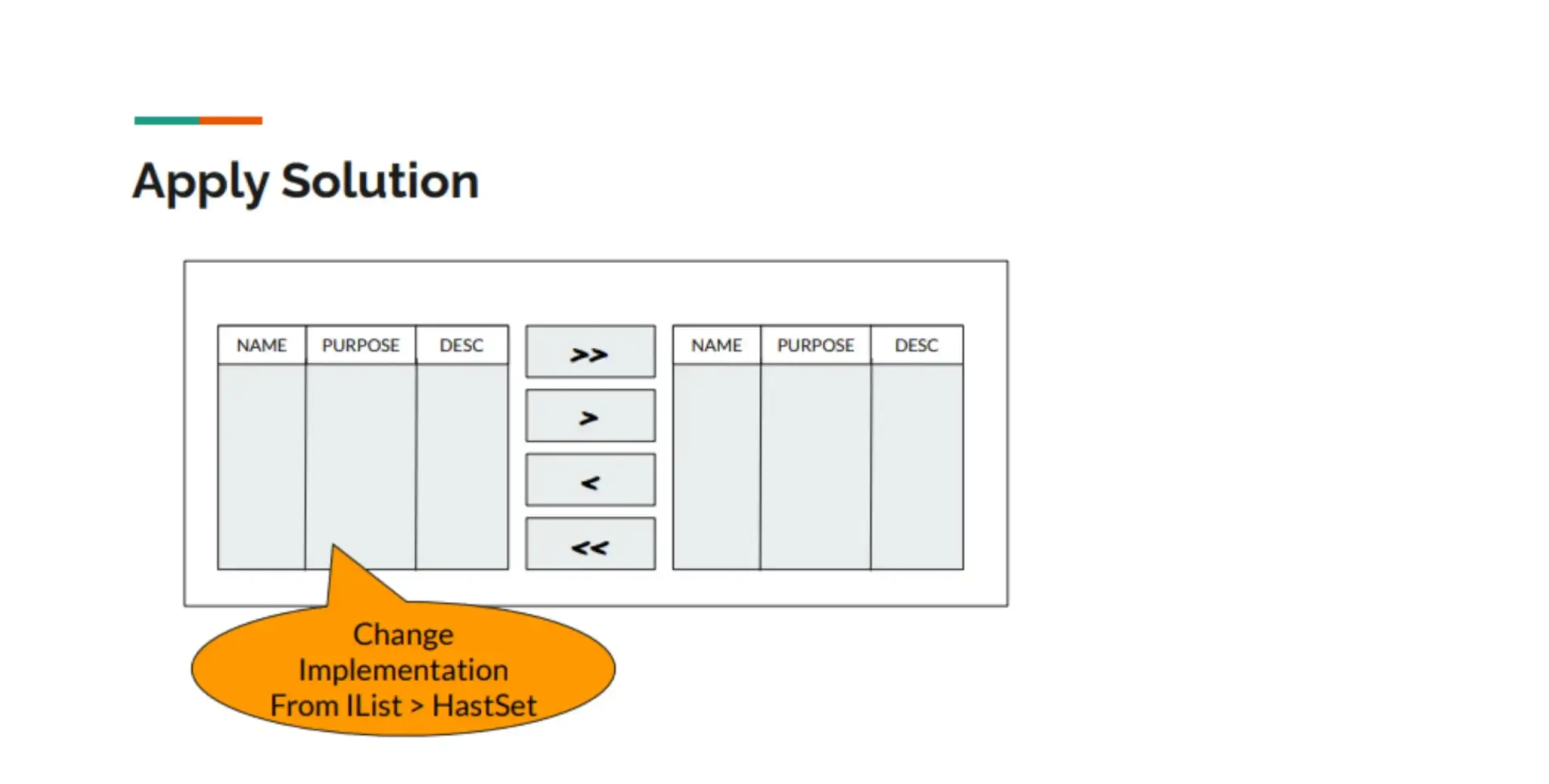
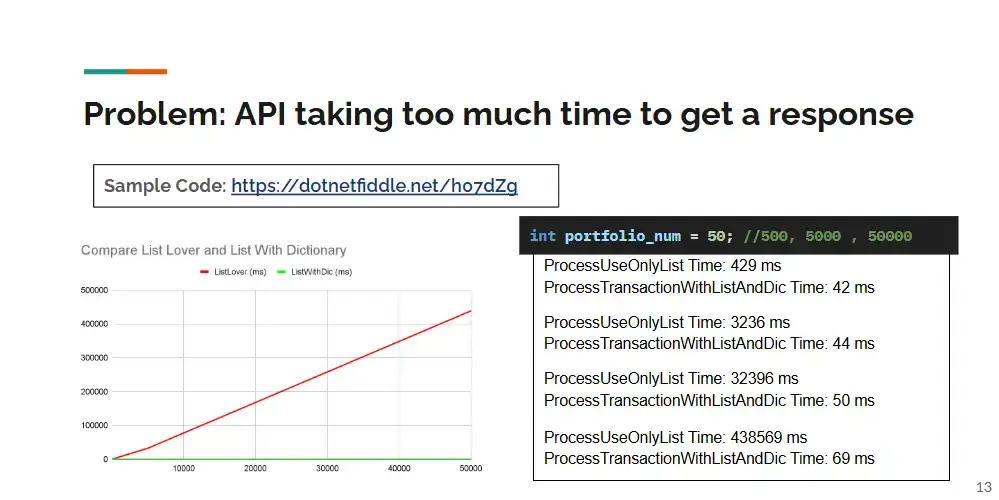
Sample Code: https://dotnetfiddle.net/MrFiYg (List vs Hash Map)
นอกจากส่วนของการเลือกใช้ Data Structure แล้ว ยังมี Step ของการ Call 3rd Party API เรา Call บ่อยๆ ในทีนี้จะเป็นตัว DevExpress มันจะมี latency เกิดขึ้น เป็นไปได้ ดึงมาทั้งหมดก่อน แล้วมา Process หยิบทีเดียว
- Old Code
int[] sourceIndex = new int[this._sourceGridView.SelectedRowsCount];
for (int row = this._sourceGridView.SelectedRowsCount - 1; row >= 0; row--){
if (_sourceGridView.GetSelectedRows()[row] >= 0){
sourceIndex[row] = this._sourceGridView.GetDataSourceRowIndex(this._sourceGridView.GetSelectedRows()[row]);
}
else{
sourceIndex[row] = this._sourceGridView.GetSelectedRows()[row];
}
}- New Code - ปรับไปแล้ว ข้อมูลที่หมื่น Record ใน Grid จากเดิมรอไป 2-3 นาที ตอนนี้แปบเดียวครับ
int[] selectedRows = this._sourceGridView.GetSelectedRows();
int[] sourceIndex = new int[selectedRows.Length];
for (int row = 0; row < selectedRows.Length; row++){
if (selectedRows[row] >= 0){
sourceIndex[row] = this._sourceGridView.GetDataSourceRowIndex(selectedRows[row]);
}
else{
sourceIndex[row] = selectedRows[row];
}
}อันนี้จริงๆเหมือนเป็นการแก้แบบ Workarounds นะ เพราะข้อมูลที่มาแสน หรือหลักล้าน มาให้เลือกทีละอัน แปลกๆอยู่ดี อาจจะต้องเอา UX/UI มาช่วยต่อครับ
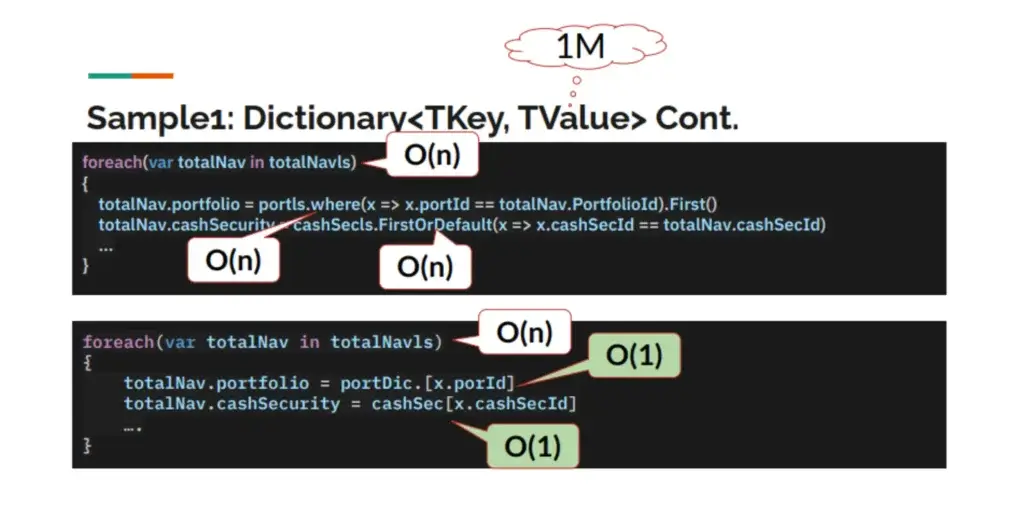
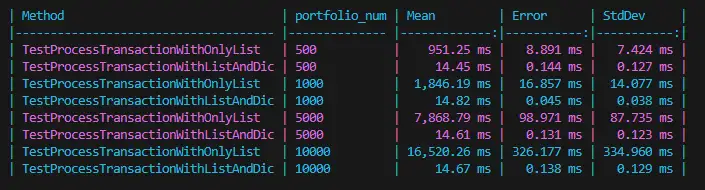
- Process ต่างๆ มันกินเวลามาขึ้น อย่างมีนัยสำคัญ เมื่อข้อมูลเพิ่มขึ้น
ทางแก้พยายามเปลี่ยน Preprocess ข้อมูลก่อน อาจะที่แบบมันเป็นแนว Lookup ให้ทำเป็น Dictionary ไว้ก่อนเข้า Loop
public static void ProcessTransactionWithListAndDic(IList<TransactionDTO> pTransactions, IDictionary<int, PortfolioDTO> pPortDic, IDictionary<int, PortPriceSouceDTO> pPortPriceSourceDic)
{
foreach (var transaction in pTransactions)
{
var portfolio = pPortDic.ContainsKey(transaction.PortfolioId) ? pPortDic[transaction.PortfolioId] : null;
if (portfolio != null)
{
// You can save or process the transaction with the portfolio here
//....
}
var portPriceSource = pPortPriceSourceDic.ContainsKey(transaction.PortfolioId) ? pPortPriceSourceDic[transaction.PortfolioId] : null;
if (portPriceSource != null)
{
// You can save or process the transaction with the portfolio here
//....
}
}
}Sample Code: https://dotnetfiddle.net/h07dZg
Summary
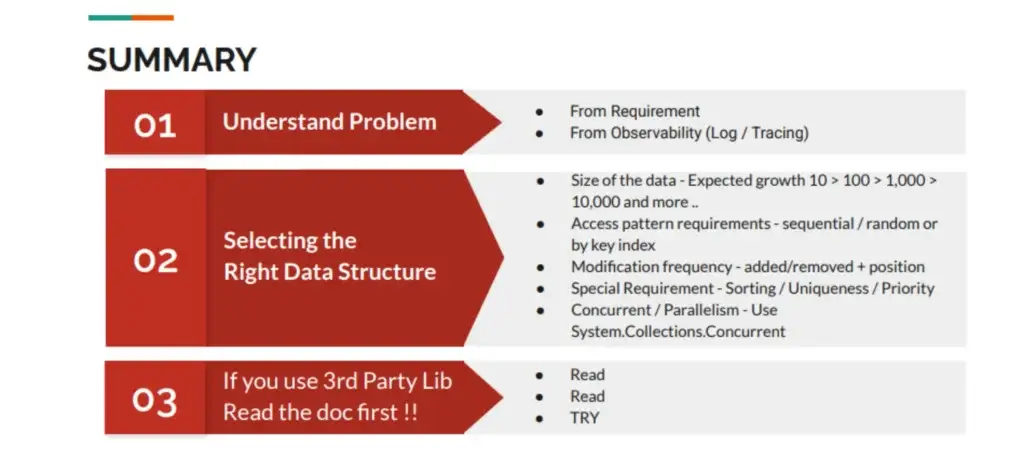
สรุปตามรูปเลย
- เราต้องเข้าใจปัญหาก่อน เพราะของผมว่ากว่าจะเจอได้ ทุกคนไปคิดว่ามันเกิดจากให้ vCPU น้อยไป หรือ Database Index ไม่เพิ่มพอต้องเพิ่ม แต่จริงแล้วมาจาก Code ที่รู้เพราะไปไล่ใส่ observability (Tracing) ในทุก Method จนเห็นว่ามันแปลกๆ
- เลือก Data Structure ให้เหมาะกับงาน ดูจาก Size / Access Pattern / ความถี่ในการแก้ไข / มันทำงาน Single Thread หรือ Multi-Thread รวมถึงพวก Constraint อื่นๆ
- ก่อนจะใช่อะไร อ่าน doc ก่อนครับ ^__^
และการเลือก Data Structure + Algorithm เป็นจุดเริ่มต้นที่ดีให้ระบบของเรา ไม่เกิดปัญหาด้าน Performance แต่มันมีอีกหลายส่วนประกอบนะ เช่น Architecture Design / Database Schema Design / You Logic เช่น Algorithm, Business, Sort / SQL ที่เขียนนี่แหละ !!!!!
ปิดท้ายด้วยตารางสรุปแนวทางการในเลือก Data Structure (Generic)

| Data Structure | Best For | Avoid When | Key Strength | Key Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Array | Fixed-size, direct indexing | Frequent size changes | Fast access | Fixed size |
| List | Dynamic collection with index access | Many inserts in middle | Flexible size | Middle insertions |
| Dictionary | Key-value lookups | Ordered data needed | Fast lookups | No ordering |
| LinkedList | Frequent inserts/deletes | Random access needed | Fast modifications | Slow lookups |
| Stack | LIFO processing | Random access needed | Simple model | Limited access pattern |
| Queue | FIFO processing | Random access needed | Simple model | Limited access pattern |
| HashSet | Unique item collection | Ordering needed | Fast lookups | No duplicates |
| SortedDictionary | Ordered key-value pairs | Huge collections with frequent changes | Ordered + lookup | Slower than Dictionary |
| SortedSet | Ordered unique items | Many duplicates needed | Ordered uniqueness | Slower than HashSet |
| PriorityQueue | Priority-based processing | FIFO/LIFO needed | Priority handling | Complex interface |
Resource: Slide / Source Code
Discover more from naiwaen@DebuggingSoft
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


