Table of Contents
ทำไมถึงต้องมี Security
เพราะการสื่อสาร (Communication) มันไม่เป็นความลับ หรือ ผู้ส่งกับผู้รับอีกต่อไป มือที่สามอ่านได้ และเอาไปทำอะไรต่อ เช่น หลอกในโอนเงิน ปลอมเป็นอีกคนเป็นต้น
จึงการเพิ่มในส่วน ciphertext ซึ่งเป็นตัวเข้ารหัสนี่เอง โดยผู้ส่งเข้ารหัส (Encryption) / ผู้รับถอดรหัส (Decryption) ตอนนี้จะเป็นต้ว
- https
- SSL/TLS
- Certificate Validation ตรวจ Cert ที่ว่าตรงกับที่ certificate authority (CA) ออกไหม
- root certificate authority
ตอนที่เรายิง request ไปยังเว็บ มันเกิดกระบวนการ Validate SSL/TLS ซึ่งมีพื้นฐานมาจาก Asymmetric cryptography (public key / private key)
Secure connection is enough?
ถึงแม้ว่ามีการเข้ารหัสของการสื่อสารแล้ว ยังไม่ปลอดภัยนะ
Secure connection ≠ trusted user
ต้องมี Authentication (เราเป็นใคร) และ Authorization (เรามีสิทธิอะไร)
- Authentication
Type of Authentication ยีนยัน เราเป็นใคร จากอะไร
- Something you know - passwords, PINs, answers (พวกคำถาม 3 ข้อสมัยก่อนก็ใช้)
- Something you have - smart cards, hardware tokens, OTP
- Something you are - fingerprints/ retina scans / facial recognition / geolocation
- Something you do - unlock patterns / typing rhythm
Authentication method มีหลายแบบ เช่น
- API Keys - ได้จากผู้ให้บริการ หรือ เราไปขอเอง แล้วเอามาแปะ ตามนี้ หรือ doc เค้ากำหนด
//ใน URL https://api.example.com/data?apikey=YOUR_API_KEY) //ใน Request Header Authorization: Bearer <<YOUR_API_KEY>> //ตัวอย่างพวก Line Notify //As part of the request body in POST requests. -ผมไม่ค่อยเจอ ไปเจออีกแบบยัดใน X-Api-Key ตรง request header
- Basic Authentication - username:password ส่วนใหญ่จะ encrypt ด้วย base64
Authorization: Basic <credentials>
- Token-Based Authentication
- OAuth
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens)
Authorization: Bearer <jwt_token>
- Authorization
Component
- Permissions สิทธิการ Action ต่างๆ CRUD ที่ทำได้ โดยอาจจะแบ่งตามหน้าจอ
- Role: Collection of Permissions เช่น พนักงาน / admin
- Policy: High-level ขึ้นไปอีก อาจจะคุมพวก Role
สำหรับระบบที่เจอกันมี Pattern 2 แบบ
- Permission-based - map user เข้ากับ Permissions แต่ละอันเลย CRUD อะไรได้
- Role-based - map user เข้ากับ Role โดยที่ Role มันจะไป map เชื่อมกับ Permissions อีกที เช่น Owner (CRUD ) / Reader (R)
JSON Web Token (JWT)
JWT - string ที่ถูกกำหนดเป็น และมาแก้ปัญหาเดิมๆของ Session ที่มันจำ Server (สมัยนี้ใครจะรู้จัก Session ไหมนะ 555) โดยตัว string เกิดจาก secret sign ด้วย
- symmetric algorithm อย่าง HMAC
- หรือ asymmetric algorithm ใช้ private (for signing) / public (for verification) key pair (RSA / ECDSA)
- Why JWT?
- Stateless Authentication - Information contained within the JWT
- Scalability - no needing to share session data ข้อจำกัดเดิมของ Session เลย มันเลยกลายเป็นว่า ถ้าไป Server ใหม่ต้องยิง Authen ใหม่
- Decentralized Issuance - Tokens can be issued and verified by multiple parties or services
- Fine-grained Authorization
- Short-lived & Expiry
- Standardized
- JWT Structure xxxxx.yyyyy.zzzzz
- Header (xxxxx) - ใช้ Algorithm อะไร
- Payload (yyyyy) - ของข้างใน อาจจะเรียกว่า Claim โดยมีข้อมูลว่าข้อมูลนี้ของ user อะไร มีสิทธิอะไรบ้าง แล้วหมดอายุตอนไหน และ onformation อื่นๆ
- Signature (zzzzz) - บอกว่าข้อมูลของ jwt นั้นถูกต้อง ไม่โดนแก้ ถุึงเรียกว่าเป็น digitally signed
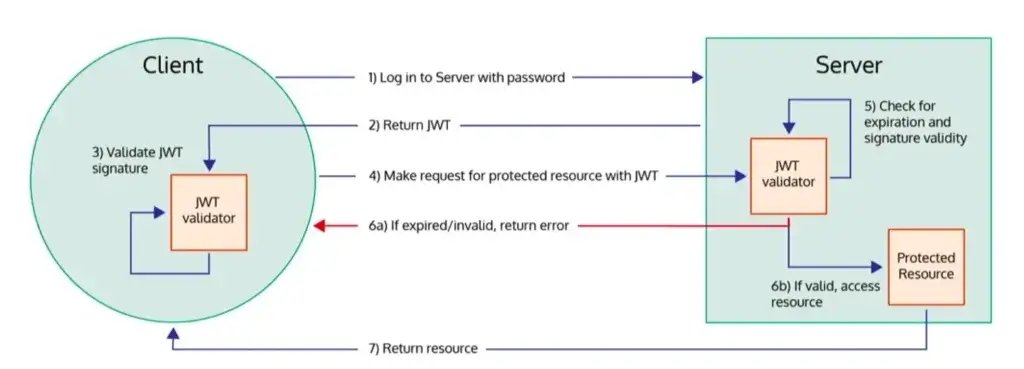
โดย flow การทำงานจะตามรูป ฝั่ง server จะมาตรวจ client ก็มีนะ แต่ไม่นิยม
- JWT - Consideration & Practices
- Transmission: encrypted channels เช่น https
- Storage: stored securely โดยเฉพาะ Client Side เพราะ ถ้าเอาไปเก็บใน Web Storage จะเจอ XSS attacks)
- Secret: เก็บของให้ดี
- symmetric signing algorithms เช่น HMAC SHA256 ระวัง secret key
- Asymmetric algorithms (e.g., RSA/ ECDSA) เก็บพวก key อย่าให้หลุด - Expiration: Short-lived ถ้า JWT หลุดไป จะมีช่วงให้โดนโจมตีได้น้อย
แต่อาจจะประสบปัญหาว่า Login บ่อย เลยมี Concept Access Token (สั้น บอกสิทธิว่าเราทำอะไรได้) / Refresh Token (ยาวหน่อย ขอ Access Token)
มีอีก Blog นะเคยเขียนไว้นานแล้ว [JWT] Idea การออกแบบ Token สำหรับ Microservice
- Implementing JWT - Access Token
Concept คล้ายกับ dotnet นะ check user > create claim > sign > access token + refresh token
- Plain Access Token learn-go/API/7JWT/1PlainJWT/server.go at main · pingkunga/learn-go (github.com)
- Echo Access Token + Refresh Token learn-go/API/7JWT/API/server.go at main · pingkunga/learn-go (github.com)
go get -u github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v5 go get github.com/labstack/echo-jwt/v4
func authHandler(c echo.Context) error {
username := c.FormValue("username")
password := c.FormValue("password")
//1.check user Throws unauthorized error (Not Good HardCode)
if username != "admin" || password != "admin" {
return echo.ErrUnauthorized
}
//2. Set custom claims
claims := &jwtCustomClaims{
"admin minda",
"admin",
"access",
jwt.RegisteredClaims{
ExpiresAt: jwt.NewNumericDate(time.Now().Add(time.Minute * 5)),
},
}
//3. Create token with claims
accessToken := jwt.NewWithClaims(jwt.SigningMethodHS256, claims)
//4. Generate encoded token and send it as response.
accessTokenString, err := accessToken.SignedString([]byte("secret"))
if err != nil {
return err
}
//2. Create refresh token
refreshTokenClaims := &jwtCustomClaims{
"admin minda",
"admin",
"refresh",
jwt.RegisteredClaims{
ExpiresAt: jwt.NewNumericDate(time.Now().Add(24 * time.Hour)), // Longer-lived
},
}
//3. Create token with claims
refreshToken := jwt.NewWithClaims(jwt.SigningMethodHS256, refreshTokenClaims)
//4. Generate encoded token and send it as response.
refreshTokenString, err := refreshToken.SignedString([]byte("secret"))
if err != nil {
return err
}
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, echo.Map{
"access_token": accessTokenString,
"refresh_token": refreshTokenString,
})
}OAUTH2.0
“Open Authorization” เป็น authorization protocol ไปใช้ Third Party Service เช่น Google / Facebook เป็นต้น โดยที่เราไม่ต้องเก็บข้อมลูเอง โดยมีจุดเด่น
- User Security - จัดการที่ Third Party Service ไม่ต้องมา share user pass ซ้ำๆ
- Simplified User Experience - ลดขั้นตอน ก็สะดวกขึ้น เช่น Register บราๆ
- Flexible Access Control - เลือก Share ข้อมูล อะไรก็ได้ ขอ Consents
- Scalability for Developers
API Security Practices
- Use Strong authentication mechanisms
- OAUTH2.0
- JWT short-lived token / Access Token + Referesh Token
- ถ้ายัง Basic Authentication หรือ API Key ให้เอา security measure อื่นๆมาประกอบ เช่น การใช้ Key/Pair มาประกอบ ยกตัวอย่าง เช่น ให้ API Key ให้รู้ว่าเป็นใคร ตอนใช้งานจริงมีเอา Private Publice มา Encrypt อีกที - Rate Limiting
- fair access ป้องกัน DDOS ให้ระบบ Stable ที่สุด
- ตัวอย่าง API Request Limti / Login Attempt / Data Upload Size Limit - Input Validation
- ป้องกัน SQL Injection และทำให้ระบบไม่เพี้ยน ตอนเอาไปทำงานในส่วนอื่นๆ
- จริงๆมันทำที่ Pattern รอได้เลยนะ พวก Email / Date Format - Data Protection
- Encryption at rest ตอนเก็บ เช่น password ก็ hash ไว้ หรือ จะเอาอีก algorithms / key มา sign ซ้ำ
- Encryption in transit ตอนนี้ https แล้วหนึ่ง - Logging and Monitoring
- ใครทำอะไร ที่ไหน อย่างไร มี Pattern อะไร
- Tools พวก SIEM / SOAR - CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)
- บอกว่า Client เข้ามาจากที่ไหน เช่น front (example.com) > back รับจาก example.com ถ้ามาจากที่อื่น reject
- ห้ามกำหนด * - Error Handling - generic error messages ไม่ต้องให้ข้อมูลพวก Runtime / Host หลุดออกมา
- Updating Dependencies - govulncheck / snyk
Discover more from naiwaen@DebuggingSoft
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.